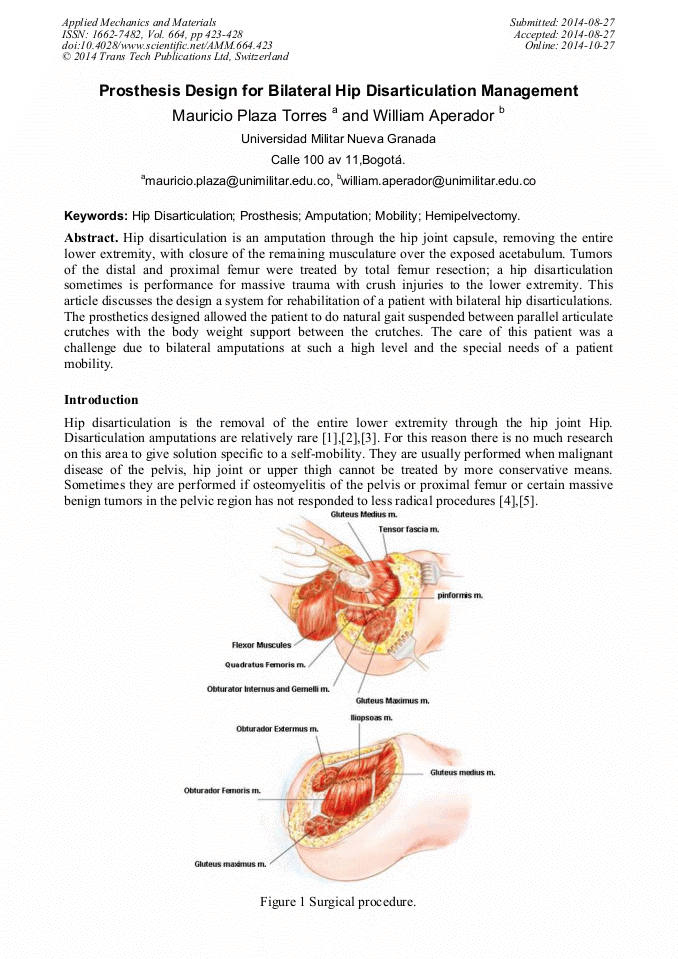
[1]
Coley BL, Higinbotham NL, Romieu C: Hemipelvectomy for tumors of bone: Report of fourteen cases. Am J Surg 1951; 82: 27-43.
DOI: 10.1016/0002-9610(51)90294-2
Google Scholar
[2]
Dankmeyer CH Jr: Prosthetic management of adult hemicorporectomy and bilateral hip disarticulation amputees. Orthot Prosthet 1981; 35: 11-18.
Google Scholar
[3]
Davis BP, Warner R, Daniel R, et al: The problem of fitting a satisfactory prosthesis following hemipelvectomy. Inter-Clin Info Bull 1964; 3: 5-9.
Google Scholar
[4]
Desio MA, Leonard JA: Above-knee prosthesis for hip disarticulation (abstract). Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1986; 67: 667-668. Foort J: Construction and fitting of the Canadian-type hip-disarticulation prosthesis. Artif Limbs 1957; 4: 39-51.
Google Scholar
[5]
Foort J. Some experience with the Canadian-type hip-disarticulation prosthesis. Artif Limbs 1957; 4: 52-70.
Google Scholar
[6]
Friedmann L. Comments and observations regarding hemipelvectomy and hemipelvectomy prosthetics. Orthot Prosthet; 21: 271-273.
Google Scholar
[7]
Giaccone V, Stack D. Temporary prosthesis for the hip-disarticulation amputee. Phys Ther; 57: 1394-1396.
DOI: 10.1093/ptj/57.12.1394
Google Scholar
[8]
Gillis L: A new prosthesis for disarticulation at the hip. J Bone Joint Surg; 50: 389-391.
Google Scholar
[9]
Glattly HW: A preliminary report on the amputee census. Artif Limbs 1963; 7: 5-10. Greene M: Four bar knee linkage analysis. Orthot Prosthet; 37: 15-24.
Google Scholar
[10]
Hampton F: A hemipelvectomy prosthesis. Artif Limbs; 8: 3-27.
Google Scholar
[11]
Hampton F: A Hemipelvectomy Prosthesis. Chicago, Northwestern University Prosthetic Research Center, p.32.
Google Scholar
[12]
Huang CT: Energy cost of ambulation with Canadian hip disarticulation prosthesis. J Med Assoc State Ala; 52: 47-48.
Google Scholar
[13]
Hutter CG: Improved type of hip-disarticulation on prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]; 35: 745-748.
DOI: 10.2106/00004623-195335030-00025
Google Scholar
[14]
Imler C, Quigley M: A technique for thermoforming hip disarticulation prosthetic sockets. J Prosthet Orthot; 3: 34-37.
DOI: 10.1097/00008526-199010000-00010
Google Scholar
[15]
Iwakura H, Abe M, Fujinaga H, et al: Locomotion of the hemipelvectomy amputee. Prosthet Orthot Int; 3: 111-114.
Google Scholar
[16]
Jay GR, Sabolich L: A bilateral above-knee/hip disarticulation fitting. Inter-Clin Info Bull; 11: 9-12.
Google Scholar
[17]
Jensen JS, Mandrup-Poulsen T: Success rate of prosthetic fitting after major amputations of the lower limb. Prosthet Orthot Int; 7: 119-122.
DOI: 10.3109/03093648309166987
Google Scholar
[18]
Lehneis HR, et al: Prosthetics Management for High Level Lower Limb Amputees. New York, Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine.
Google Scholar
[19]
Leppanen RE: A temporary prosthesis for hip disarticulation. Phys Ther; 49: 987-990.
DOI: 10.1093/ptj/49.9.987
Google Scholar
[20]
Littig DH, Lundt JE: The UCLA anatomical hip disarticulation prosthesis. Clin Prosthet Orthot; 12: 114-118.
Google Scholar
[21]
Lyquist E: Canadian-type socket for a hemipelvectomy. Artif Limbs; 5: 130-132.
Google Scholar
[22]
The flexible socket system as applied to the hip disarticulation amputee. Orthot Prosthet ; 39: 44-47.
Google Scholar
[23]
Marx HW: Some experience in hemipelvectomy prosthetics. Orthot Prosthet; 00: 259-270.
Google Scholar
[24]
McLaurin CA: Hip Disarticulation Prosthesis, Report No. 15. Toronto, Canada, Prosthetic Services Centre, Department of Veterans Affairs.
Google Scholar
[25]
Pinzur MS, et al: An easy-to-fabricate modified hip disarticulation temporary prosthesis (technical note). Orthot Prosthet; 40: 58-60.
Google Scholar
[26]
Radcliffe CW: The biomechanics of the Canadian-type hip-disarticulation prosthesis. Artif Limbs; 4: 29-38.
Google Scholar
[27]
Sabolich J, Guth T: The CAT-CAM-HD. A new design for hip disarticulation patients. Clin Prosthet Orthot; 12: 119-122.
Google Scholar
[28]
Shurr DG, Cook TM, Buckwalter JA, et al: Hip disarticulation: A prosthetic follow-up. Orthot Prosthet; 37: 50-57.
Google Scholar
[29]
Simons BC, Lehman JF, Taylor H, et al: Prosthetic management of hemicorporectomy. Orthot Prosthet; 22: 63-68.
Google Scholar
[30]
Solomonidis SE, Loughran AJ, Taylor J, et al: Biomechanics of the hip disarticulation prosthesis. Prosthet Orthot 1nt; 1: 13-18.
Google Scholar
[31]
Van der Waarde T: Ottawa experience with hip disarticulation prostheses. Orthot Prosthet; 38: 29-33.
Google Scholar
[32]
Waters RL, et al: Energy costs of walking of amputees: The influence of level of amputation. J Bone Joint Surg [Am]; 58: 46.
Google Scholar