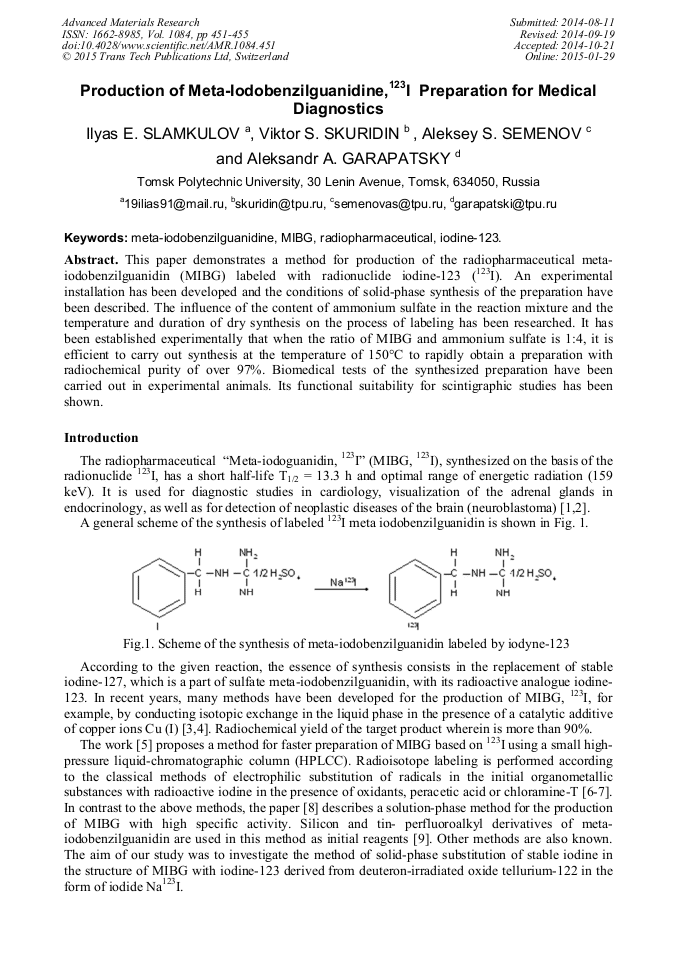
[1]
A.R. Wafelman, C.A. Hoefnagel, J.H. Beijnen, Chromatographic determination of the radiochemical purity of [131I]MIBG infusion fluids: a comparison and discussion of the chromatographic characteristics using three different techniques, J. Applied Radiation and Isotopes 44 (1993).
DOI: 10.1016/0969-8043(93)90029-a
Google Scholar
[2]
W.H. Bierwalters, Radioiodine therapy of thyroid disease, J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 14 (1987) 183-185.
Google Scholar
[3]
G. Vaidyanathan, M.R. Zalutsky, No-carrier-added synthesis of a 4-methyl-substituted meta-iodobenzylguanidine analogue, J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 44 (1993) 621-623.
DOI: 10.1016/0969-8043(93)90179-e
Google Scholar
[4]
T. Yassin, M. Bakir, Preparation, purification and quality control of 131I-m-iodobenzyl-guanidine (MIBG)*, J. Radioanalytic. Nucl. Chem. 3 (2003) 635-637.
Google Scholar
[5]
A. Katsifis, V. Parazian, A rapid and efficient preparation of [123I] radiopharmaceuticals using a small HPLC (Rocket) column , J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 64 (2006) 27-31.
DOI: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2005.06.006
Google Scholar
[6]
R. Mastrangelo, S. Tornesello, 131I-metaiodobenzylguanidine in the treatment of neuroblastoma, J. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 31 (1998) 22-24.
DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1096-911x(199807)31:1<22::aid-mpo5>3.0.co;2-1
Google Scholar
[7]
G. Vaidyanathan, M. Zalutsky, No-carrier-added meta-[123I]iodobenzylguanidine: synthesis and preliminary evaluation, J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 22 (1995) 61-64.
DOI: 10.1016/0969-8051(94)00078-x
Google Scholar
[8]
A. Donovan, J. Valliant, A convenient solution-phase method for the preparation of meta-iodobenzylguanidine in high effective specific activity, J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 35 (2008) 741-744.
DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2008.07.006
Google Scholar
[9]
A. Donovan, J. Forbes, P. Dorff, P. Schaffer, J. Babich, J.F. Valliant, A new strategy for preparing molecular imaging and therapy agents using fluorine-rich (fluorous) soluble supports , J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128 (2006) 36-40.
DOI: 10.1021/ja0600375
Google Scholar
[10]
V.S. Scuridin, Methods and technology for radiopharmaceuticals preparation: tutorial, Tomsk Polytechnic University, Tomsk, Publishing house of TPU, 2012 (in Russian).
Google Scholar
[11]
A.S. Semenov, V.S. Skuridin, V.M. Golovkov, The preparation radiopharmaceutical meta-iodobenzilguanidine radioiodinated, J. Izvestia Vyshich Uchebnych Zavedeniy. Fizika. 54 (2011) 310-314 (in Russian).
Google Scholar
[12]
A.A. Garapatski, V.Y. Kаsakov, N.V. Thien, The Gamma-Ray Scanner of a Chromatographic Plate for Determining the Radiochemical Purity of Radiopharmaceuticals, In Proc. of the 7th International Forum on Strategic Technology (IFOST). 2 (2012).
DOI: 10.1109/ifost.2012.6357818
Google Scholar