p.1477
p.1482
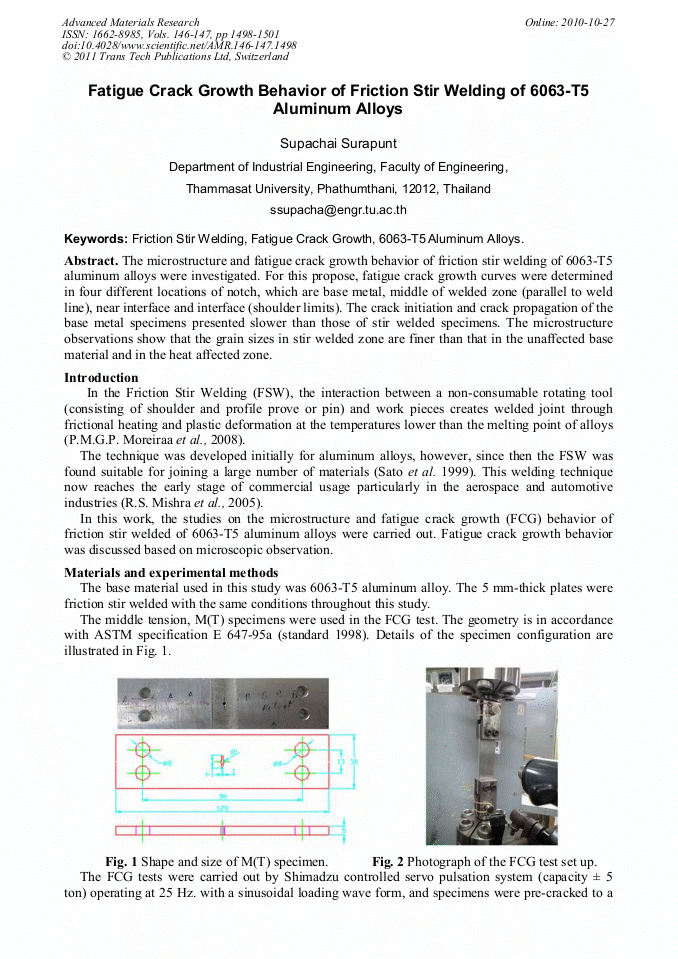
p.1486
p.1491
p.1498
p.1502
p.1506
p.1510
p.1514
Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior of Friction Stir Welding of 6063-T5 Aluminum Alloys
Abstract:
The microstructure and fatigue crack growth behavior of friction stir welding of 6063-T5 aluminum alloys were investigated. For this propose, fatigue crack growth curves were determined in four different locations of notch, which are base metal, middle of welded zone (parallel to weld line), near interface and interface (shoulder limits). The crack initiation and crack propagation of the base metal specimens presented slower than those of stir welded specimens. The microstructure observations show that the grain sizes in stir welded zone are finer than that in the unaffected base material and in the heat affected zone.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1498-1501
Citation:
Online since:
October 2010
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: