p.1569
p.1574
p.1579
p.1586
p.1590
p.1595
p.1600
p.1604
p.1609
Analysis of Formed Platelet Thermal Wrinkling in Platelet Transpiration Cooling
Abstract:
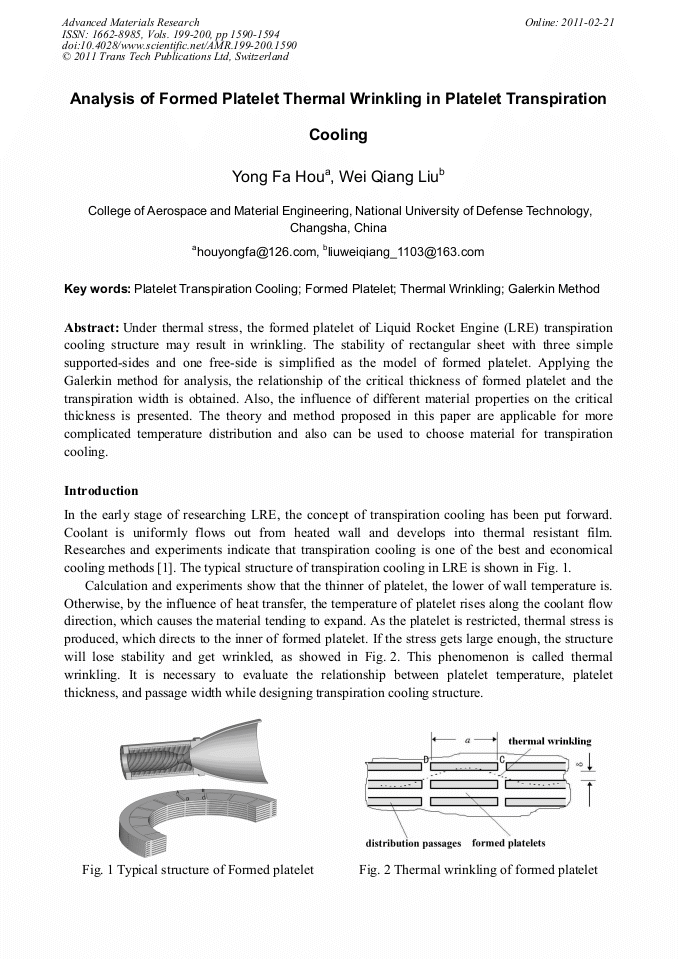
Under thermal stress, the formed platelet of Liquid Rocket Engine (LRE) transpiration cooling structure may result in wrinkling. The stability of rectangular sheet with three simple supported-sides and one free-side is simplified as the model of formed platelet. Applying the Galerkin method for analysis, the relationship of the critical thickness of formed platelet and the transpiration width is obtained. Also, the influence of different material properties on the critical thickness is presented. The theory and method proposed in this paper are applicable for more complicated temperature distribution and also can be used to choose material for transpiration cooling.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1590-1594
Citation:
Online since:
February 2011
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: