p.125
p.129
p.134
p.138
p.144
p.148
p.152
p.156
p.160
Numerical Modeling of an End-Hall Ion Source
Abstract:
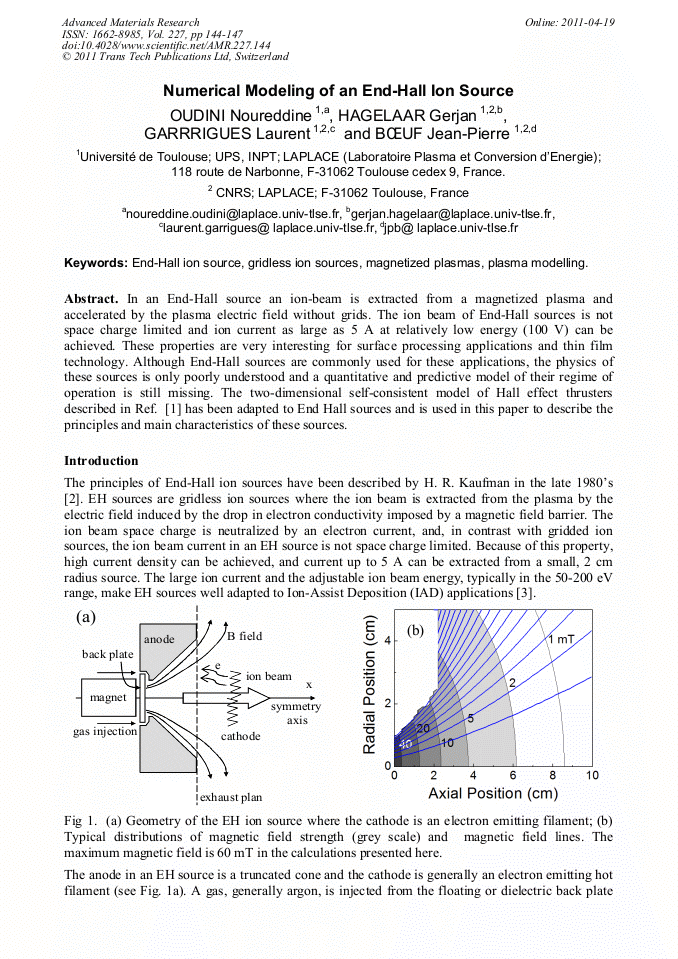
In an End-Hall source an ion-beam is extracted from a magnetized plasma and accelerated by the plasma electric field without grids. The ion beam of End-Hall sources is not space charge limited and ion current as large as 5 A at relatively low energy (100 V) can be achieved. These properties are very interesting for surface processing applications and thin film technology. Although End-Hall sources are commonly used for these applications, the physics of these sources is only poorly understood and a quantitative and predictive model of their regime of operation is still missing. The two-dimensional self-consistent model of Hall effect thrusters described in Ref. [1] has been adapted to End Hall sources and is used in this paper to describe the principles and main characteristics of these sources.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
144-147
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
April 2011
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: