p.1055
p.1060
p.1066
p.1071
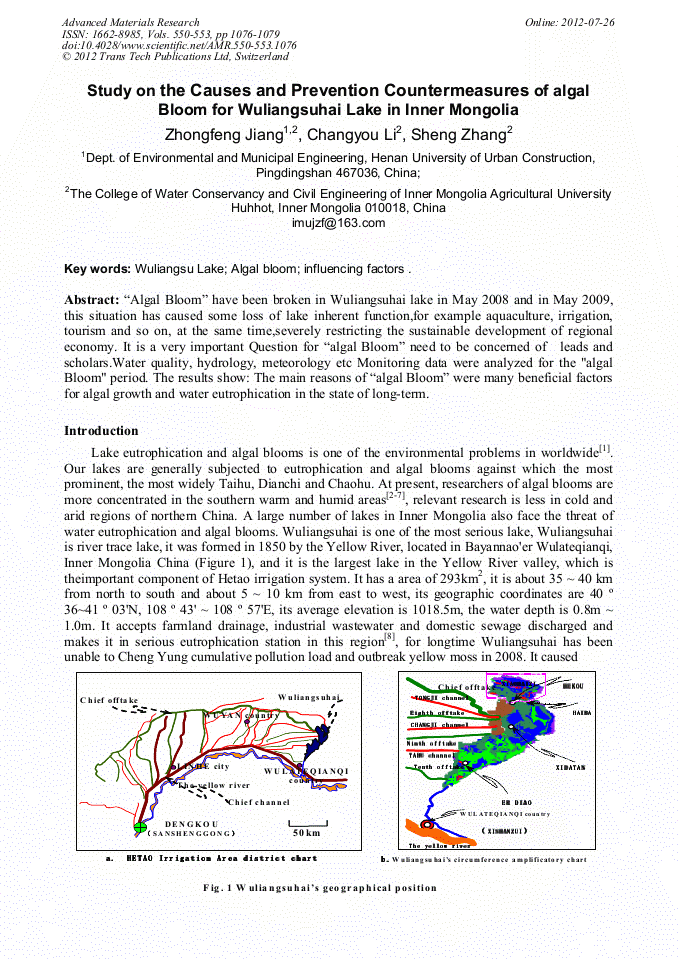
p.1076
p.1080
p.1085
p.1090
p.1094
Study on the Causes and Prevention Countermeasures of Algal Bloom for Wuliangsuhai Lake in Inner Mongolia
Abstract:
“Algal Bloom” have been broken in Wuliangsuhai lake in May 2008 and in May 2009, this situation has caused some loss of lake inherent function,for example aquaculture, irrigation, tourism and so on, at the same time,severely restricting the sustainable development of regional economy. It is a very important Question for “algal Bloom” need to be concerned of leads and scholars.Water quality, hydrology, meteorology etc Monitoring data were analyzed for the "algal Bloom" period. The results show: The main reasons of “algal Bloom” were many beneficial factors for algal growth and water eutrophication in the state of long-term.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1076-1079
Citation:
Online since:
July 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: