p.1342
p.1348
p.1354
p.1361
p.1365
p.1373
p.1378
p.1383
p.1390
A Machine Vision-Based Heating Control Design for the Microwave Maintenance Vehicle
Abstract:
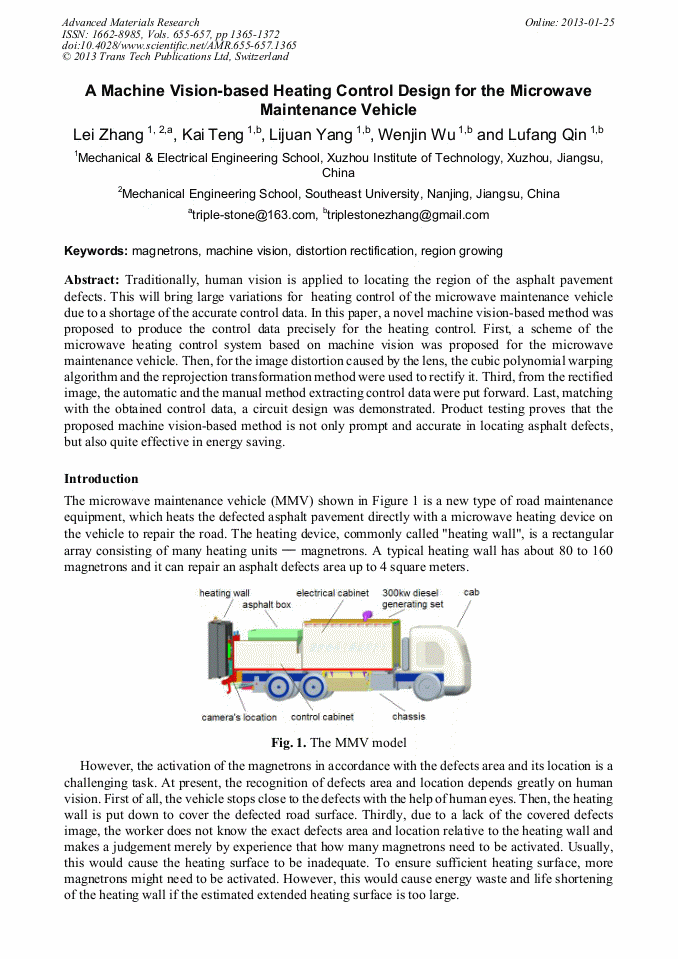
Traditionally, human vision is applied to locating the region of the asphalt pavement defects. This will bring large variations for heating control of the microwave maintenance vehicle due to a shortage of the accurate control data. In this paper, a novel machine vision-based method was proposed to produce the control data precisely for the heating control. First, a scheme of the microwave heating control system based on machine vision was proposed for the microwave maintenance vehicle. Then, for the image distortion caused by the lens, the cubic polynomial warping algorithm and the reprojection transformation method were used to rectify it. Third, from the rectified image, the automatic and the manual method extracting control data were put forward. Last, matching with the obtained control data, a circuit design was demonstrated. Product testing proves that the proposed machine vision-based method is not only prompt and accurate in locating asphalt defects, but also quite effective in energy saving.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1365-1372
Citation:
Online since:
January 2013
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: