p.1724
p.1732
p.1739
p.1744
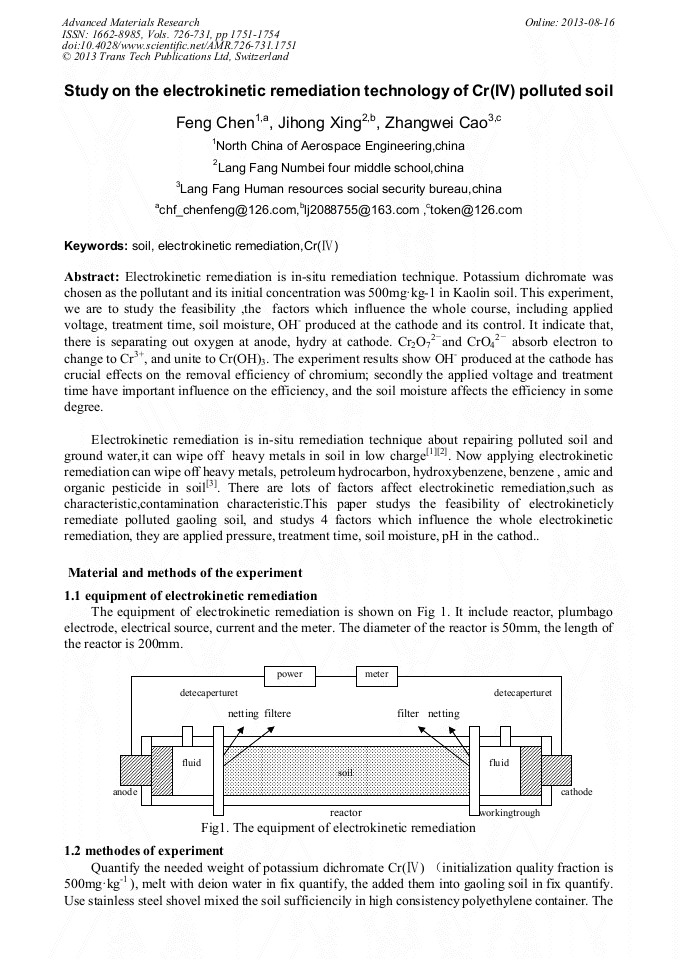
p.1751
p.1755
p.1760
p.1764
p.1770
Study on the Electrokinetic Remediation Technology of Cr (VI) Polluted Soil
Abstract:
Electrokinetic remediation is in-situ remediation technique. Potassium dichromate was chosen as the pollutant and its initial concentration was 500mg·kg-1 in Kaolin soil. This experiment, we are to study the feasibility ,the factors which influence the whole course, including applied voltage, treatment time, soil moisture, OH- produced at the cathode and its control. It indicate that, there is separating out oxygen at anode, hydry at cathode. Cr2O72-and CrO42- absorb electron to change to Cr3+, and unite to Cr (OH)3. The experiment results show OH- produced at the cathode has crucial effects on the removal efficiency of chromium; secondly the applied voltage and treatment time have important influence on the efficiency, and the soil moisture affects the efficiency in some degree.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1751-1754
Citation:
Online since:
August 2013
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: