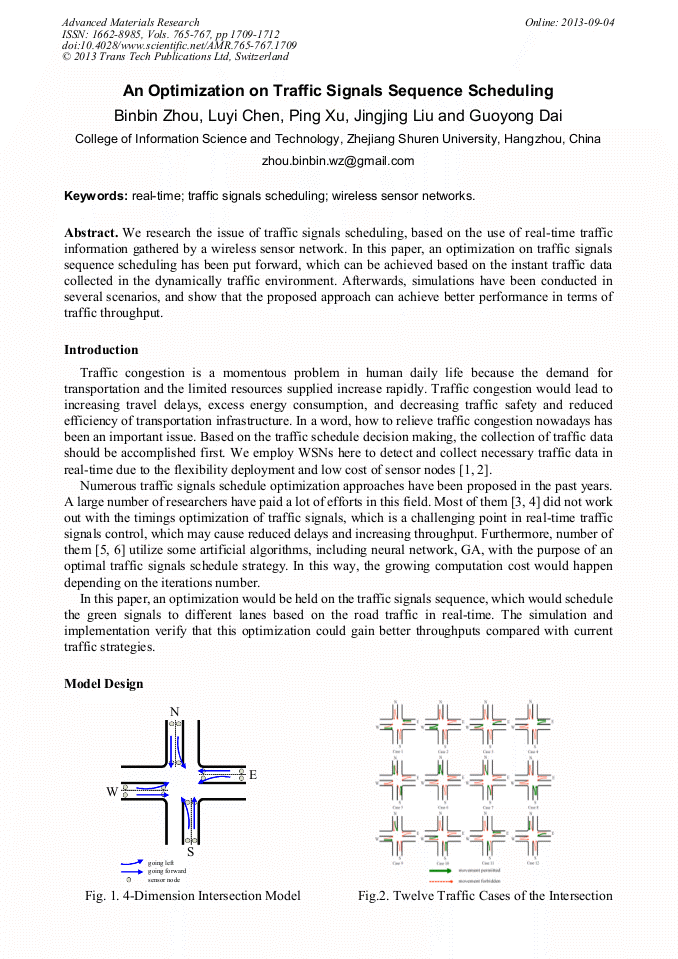
[1]
W. Chen, L. Chen, Z. Chen, and S. Tu, Wits: A wireless sensor network for intelligent transportation system, In Proceedings of the First International Multi-Symposiums on Computer and Computational Sciences, (2006).
DOI: 10.1109/imsccs.2006.286
Google Scholar
[2]
A summary of vehicle detection and surveillance technologies use in intelligent transportation systems, The Vehicle Detector Clearinghouse, (2007).
Google Scholar
[3]
C. P. Pappis and E. H. Mamdani, A fuzzy logic controller for a traffic junction, In IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, (1977).
DOI: 10.1109/tsmc.1977.4309605
Google Scholar
[4]
M. B. Trabia, M. S. Kaseko, and M. Ande, A two-stage fuzzy logic controller for traffic signals, In Transportation Research Part C, (1999).
DOI: 10.1016/s0968-090x(99)00026-1
Google Scholar
[5]
T. L. Thorpe and C. Andersson, Traffic light control using sarsa with three state representations, In Technical report, IBM Corporation, 1996. Proceeding of FUZZIEEE, volume 1, pages 296–300, (2002).
Google Scholar
[6]
B. Abdulhai, R. Pringle, and G. J. Karakoulas, Reinforcement learning for true adaptive traffic signal control, In Journal of Transportation Engineering, volume 129, pages 278–285, (2003).
DOI: 10.1061/(asce)0733-947x(2003)129:3(278)
Google Scholar
[7]
B. Zhou, J. Cao, X. Zeng, and H. Wu, Adaptive traffic light control in wireless sensor network-based intelligent transportation system, In IEEE 72nd Vehicular Technology Conference, Ottawa, Canada, (2010).
DOI: 10.1109/vetecf.2010.5594435
Google Scholar
[8]
B. Zhou, J. Cao, and H. Wu, Adaptive traffic light control of multiple intersections in WSN-based ITS, In IEEE 73rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Budapest, Hungary, (2011).
DOI: 10.1109/vetecs.2011.5956434
Google Scholar
[9]
B. Zhou, J. Cao and L. Bai, Adaptive Traffic Light Control in WSN-based ITS, LAP Publishers, March (2012).
Google Scholar
[10]
B. Zhou, P. Xu, L. Chen, J. Liu and G. Dai, An Intelligent Traffic signals Schedule Approach using WSNs, In 2013 International Conference on Applied Mathematics, Computer Simulation, Optimization and Algorithms, Shenyang, China, (2013).
Google Scholar
[11]
B. Zhou, A Real-time Traffic signals Scheduling Strategy, In 2nd International Conference on Industrial Electronics, Mechanical Engineering and Informatization, Shijiazhuang, China, (2013).
Google Scholar
[12]
http: /www. openstreetmap. org.
Google Scholar