p.545
p.551
p.557
p.563
p.569
p.575
p.580
p.585
p.591
Micro Polishing of Tungsten Carbide Using Magnetostrictive Vibrating Polisher
Abstract:
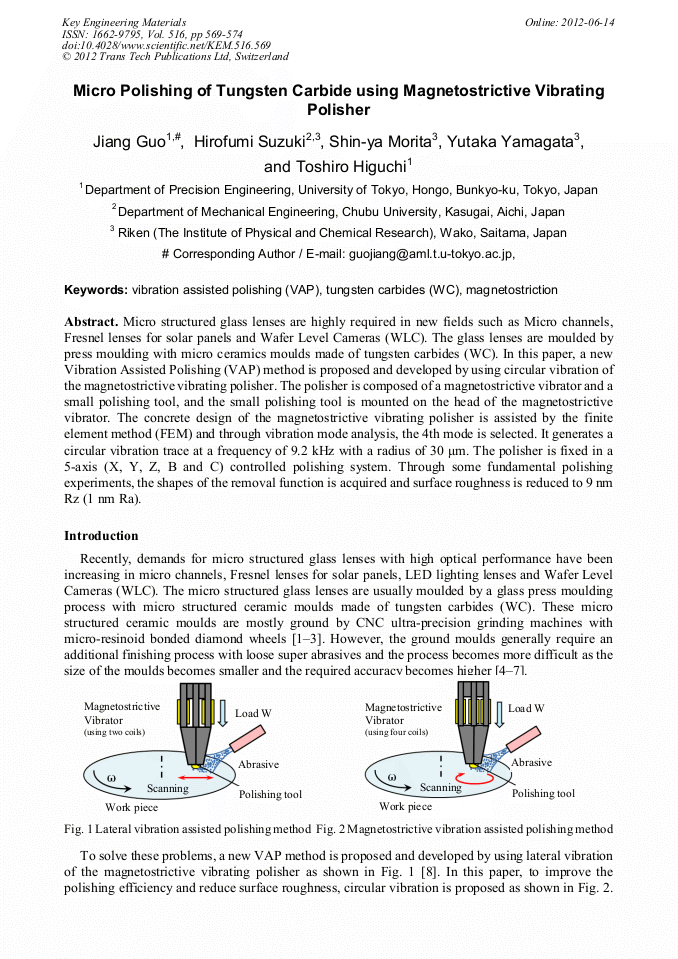
Micro structured glass lenses are highly required in new fields such as Micro channels, Fresnel lenses for solar panels and Wafer Level Cameras (WLC). The glass lenses are moulded bypress moulding with micro ceramics moulds made of tungsten carbides (WC). In this paper, a new Vibration Assisted Polishing (VAP) method is proposed and developed by using circular vibration of the magnetostrictive vibrating polisher. The polisher is composed of a magnetostrictive vibrator and a small polishing tool, and the small polishing tool is mounted on the head of the magnetostrictive vibrator. The concrete design of the magnetostrictive vibrating polisher is assisted by the finite element method (FEM) and through vibration mode analysis, the 4th mode is selected. It generates a circular vibration trace at a frequency of 9.2 kHz with a radius of 30 μm. The polisher is fixed in a 5-axis (X, Y, Z, B and C) controlled polishing system. Through some fundamental polishing experiments, the shapes of the removal function is acquired and surface roughness is reduced to 9 nm Rz (1 nm Ra).
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
569-574
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
June 2012
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: