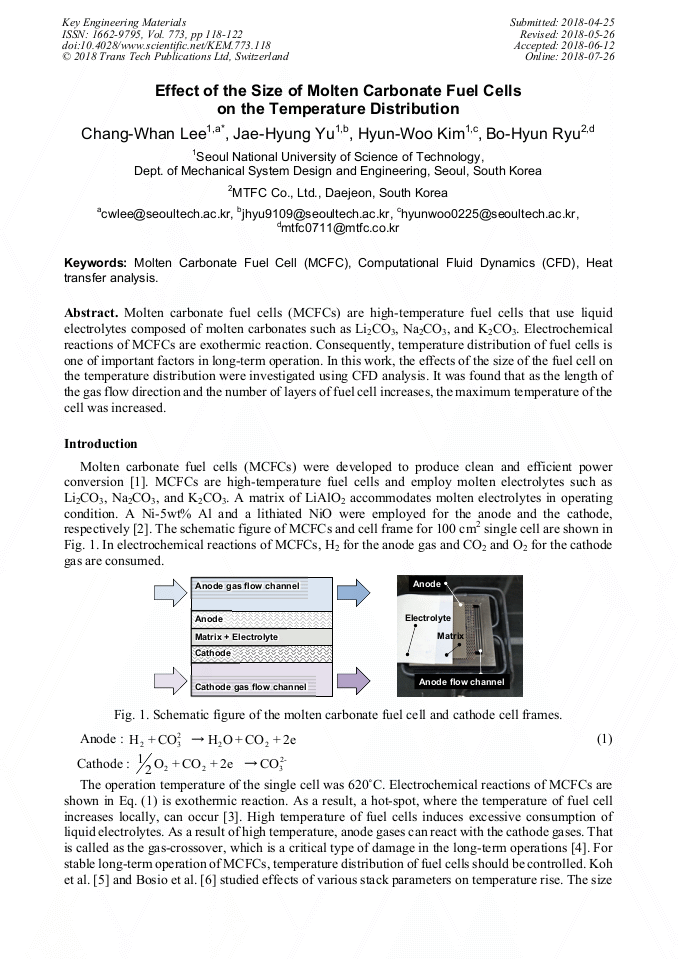
[1]
X. Li. Principles of fuel cells New York: Taylor & Francis Group; (2005).
Google Scholar
[2]
C. W. Lee, M. Lee, M. J. Lee, S. C. Chang, S. P. Yoon, H. C. Ham, Effect of the flow directions on a 100 cm2 MCFC single cell with internal flow channels, Int. J. Hydr. Energ. 41 (2016) 18747-18760.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.188
Google Scholar
[3]
C. Yuh, J. Colpetzer, K. Dickson, M. Farooque, G. Xu, Carbonate fuel cell materials, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 15 (2006) 457-462.
DOI: 10.1361/105994906x117305
Google Scholar
[4]
Y. J. Kim, I. G. Chang, T. W. Lee, M. K. Chung, Effects of relative gas flow direction in the anode and cathode on the performance characteristics of a Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell, Fuel, 89 (2010) 1019-1028.
DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.10.027
Google Scholar
[5]
J. H. Koh, B. S. Kang, H. C. Lim, Effect of various stack parameters on temperature rise in molten carbonate fuel cell stack operation, J. Power Source. 91 (2000) 161-171.
DOI: 10.1016/s0378-7753(00)00463-8
Google Scholar
[6]
B. Bosio, P. Costamagna, F. Parodi. Modeling and experimentation of molten carbonate fuel cell reactors in a scale-up process. Chem. Eng. Sci. 54(13–14) (1999) 2907-2916.
DOI: 10.1016/s0009-2509(98)00414-x
Google Scholar
[7]
C. Yuh, J. Selman, The Polarization of Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell Electrodes I. Analysis of Steady‐State Polarization Data, J. Electrochem. Soc. 138 (1991) 3642-3648.
DOI: 10.1149/1.2085473
Google Scholar
[8]
H. Kim, J. Bae, D. Choi. An analysis for a molten carbonate fuel cell of complex geometry using three-dimensional transport equations with electrochemical reactions. Int. J. Hydr. Energ. 38(11) (2013) 4782-4791.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.01.061
Google Scholar
[9]
S. Y. Lee, D. H. Kim, H. C. Lim, G. Y. Chung. Mathematical modeling of a molten carbonate fuel cell (MCFC) stack. Int. J. Hydr. Energ. 35(23) (2010) 13096-13103.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.04.070
Google Scholar
[10]
COMSOL Inc., COMSOL Multiphysics v5.3 (2017).
Google Scholar