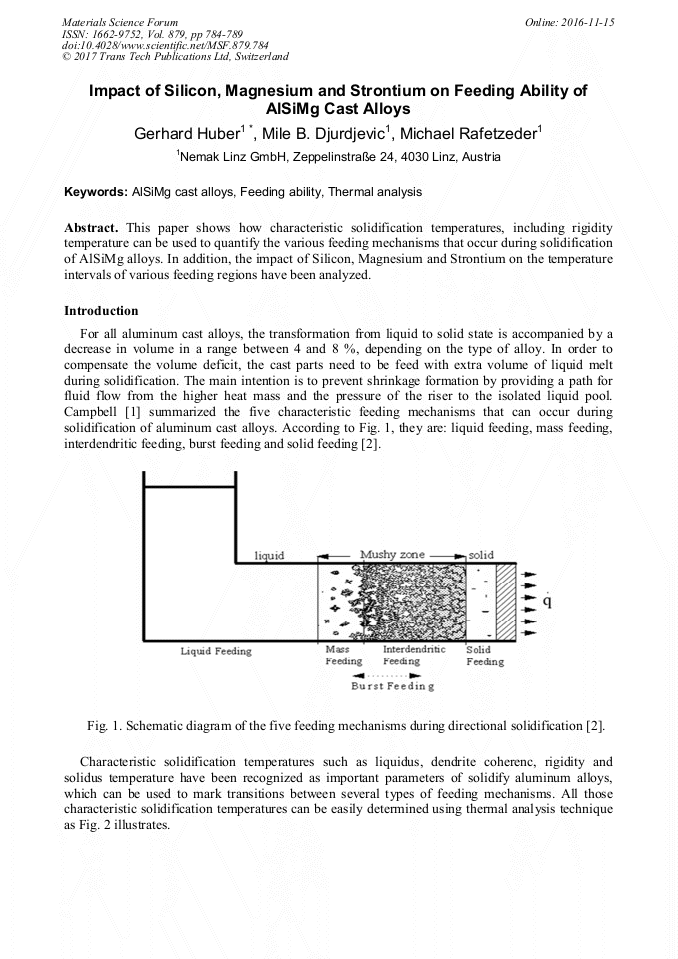
[1]
J. Campbell, Feeding Mechanisms in Castings,. AFS Cast Metal Research Journal, 1969. 5: pp.1-8.
Google Scholar
[2]
C.M. Gourlay and A.K. Dahle, The five feeding mechanisms, Shape Casting: The John Campbell Symposium Edited by Murat Tiryakioglu and Paul N. Crepeau TMS (The Minerals, Metals, & Materials Society), 2005, pp.93-102.
Google Scholar
[3]
A. Cibula The Mechanism of Grain Refinement of Sand Castings in Aluminum Alloys, J. Ins. Metals vol. 76, p.312, 1949 Nr. 50.
Google Scholar
[4]
P.B. Crossley and L.F. Mondolfo, The Modification of Aluminum Silicon Alloys, Modern Casting vol. 49, p.53/64, (1966).
Google Scholar
[5]
L. Bäckerud et al.; Solidification Characteristics of Aluminum Alloys, AFS/SKANALUMINIUM, Oslo, Volume 1 to 3, (1986).
Google Scholar
[6]
R. Krohn; Thermal analysis: Metallurgical Thumb printing, Modern Casting, March 1985, p.1−7.
Google Scholar
[7]
J.E. Gruzleski, B.M. Closset; The treatment of liquid aluminum-silicon alloys", American Foundryman, s Society, Inc. Des Plaines, Illinois, USA, (1990).
Google Scholar
[8]
N. Tenekedjiev, H. Mulazimoglu, B. Closset, J. Gruzleski; Microstructures and Thermal Analysis of Strontium-Treated Aluminum-Silicon Alloys", American Foundryman, s Society, Inc. Des Plaines, Illinois, USA, 1995 p.40−41.
Google Scholar
[9]
L. Ananthanarayanan, J.E. Gruzleski; Thermal Analysis Studies on the Effect of Cooling Rate on the Microstructure of the 319 Aluminium Alloy, AFS Transactions, 141, 1992 pp.383-391.
Google Scholar
[10]
D. Sparkman; Microstructure by Thermal Analysis, AFS Transactions, Paper 11-068, 119, 2011 pp.413-420.
Google Scholar
[11]
M. B. Djurdjevic and G. Huber; "Determination of Rigidity Point/Temperature using Thermal analysis Method and Mechanical Technique, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 590, 2014, pp.500-506.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.020
Google Scholar
[12]
W. Michel. and S, Engler; Speisungskinetik von Aluminum-Silizium Gußlegierungen, Giesserei 75, Nr. 14, 1988, pp.445-448.
Google Scholar
[13]
W. Michel and S, Engler; Erstarrungsmorphologie und Speisungsablauf von Aluminium-Silizium Legierungen bei Kokillenguß, Giesserei 77, Nr. 3, 1990, pp.79-82.
Google Scholar
[14]
P. Pucher, H. Böttcher, J. Hübler, H. Kaufmann, H. Antrekowisch and P. Uggowitzer: Einfluss der Legierungszusammensetzung auf das Speisungsverhalten der Recyclinglegierung A226 (AlSi9Cu3) im Sand und Kokillenguss, Giesserei 98, Nr. 7 2011, pp.34-44.
Google Scholar
[15]
M. Djurdjevic, G. Huber, H. Zak and B. Tonn, Effect of Silicon on the Feeding Ability in Binary Al-Si Alloys, unpublished paper.
Google Scholar
[16]
J. Pavlovic-Krstic, Impact of casting parameters and chemical composition on the solidification behavior of AlSiCu hypoeutectic alloys, PhD Theses, Otto-von-Guericke-University Magdeburg, Germany, March (2010).
Google Scholar
[17]
A. T. Joenues, The Role of Magnesium on Eutectic Silicon Microstructure, PhD Theses, McGill University, Montreal Canada, March (1991).
Google Scholar