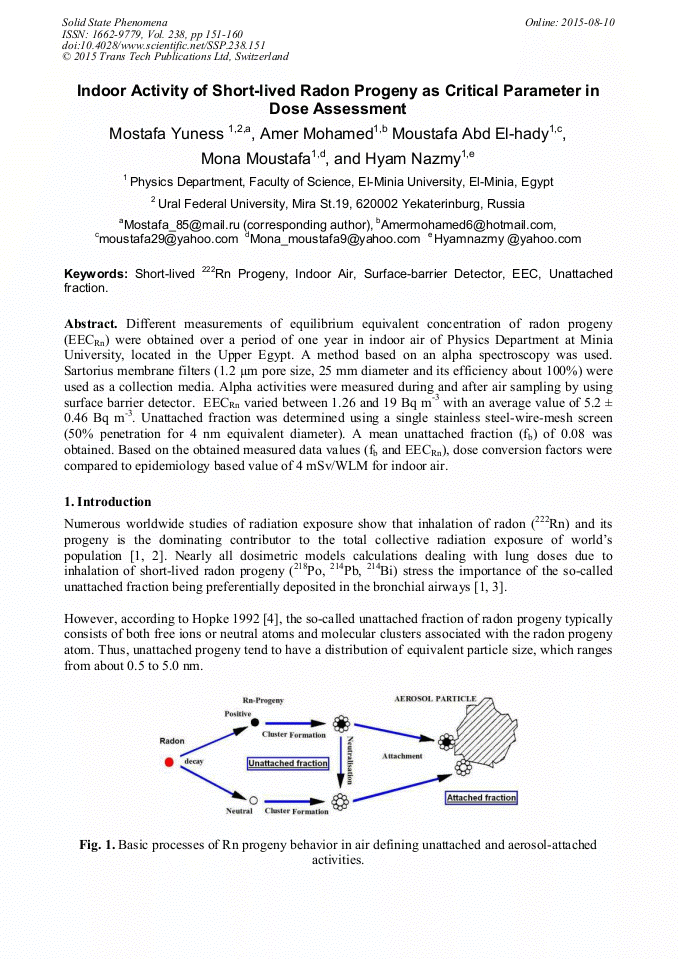
[1]
United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation. (UNSCEAR), Sources, effects and risks of ionizing radiation. Report to the General Assembly, with annexes. United Nations Publications, New York, (1993).
DOI: 10.18356/55345362-en
Google Scholar
[2]
United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR), sources and effects of ionizing radiations. Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes. United Nations, New York, (2000).
DOI: 10.18356/28d343af-en
Google Scholar
[3]
A.C. James, F.T. Cross, J.S. Durham, J. Briant, P. KGehr, R. Masse, Dosimetry model for bronchial and extrathoracic tissues of the respiratory tract, Radiation Protection Dosimetry 37 (1991) 221-230.
DOI: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a081055
Google Scholar
[4]
P.K. Hopke, Some thoughts on the 'Unattached', fraction of radon decay products. Health Physics, 63 (1992) 209-212.
DOI: 10.1097/00004032-199208000-00011
Google Scholar
[5]
International Commission on Radiological Protection, ICRP, Lung cancer risk from indoor exposure to radon daughters, Pergamon Press, Oxford; ICRP Publication, 17(1) ICRP Publication 50, (1987).
DOI: 10.3109/02841868709113723
Google Scholar
[6]
International Commission on Radiological Protection, ICRP, Protection against Radon-222 at Home and at Work. Pergamon Press, Oxford, ICRP Publication, 65 (1994 a, b).
DOI: 10.1080/09553009414551371
Google Scholar
[7]
J. Vaupotič, Nanosize radon short-lived decay products in the air of the Postojna Cave, Science of the Total Environment 393 (2008) 27.
DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.12.022
Google Scholar
[8]
M. Shimo, Y. Ikebe, Measurements of radon and its short-lived decay products and unattached fraction in air. Radiation Protection Dosimetry 8 (1984) 209–214.
DOI: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a083056
Google Scholar
[9]
A. Reineking, K.H. Becker, J. Porstendörfer, Measurements of the unattached fractions of radon daughters in houses. The Science of the Total Environment 45 (1985) 261–270.
DOI: 10.1016/0048-9697(85)90227-x
Google Scholar
[10]
A. Reineking, K.H. Becker, J. Porstendörfer, Measurements of activity size distributions of the short-lived radon daughters in the indoor and outdoor environment, Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 24 (1988) 245-250.
DOI: 10.1093/rpd/24.1-4.245
Google Scholar
[11]
A. Reineking, K.J. Porstendörfer, Unattached fraction of short-lived Rn decay products in indoor and outdoor environments: an improved single-screen method and results. Health Physcis 58 (1990) 715–727.
DOI: 10.1097/00004032-199006000-00003
Google Scholar
[12]
J. Porstendörfer, A. Reineking, Indoor behaviour and characteristics of radon progeny. Radiation Protection Dosimetry 45 (1992) 303–311.
DOI: 10.1093/rpd/45.1-4.303
Google Scholar
[13]
J. Porstendörfer, Behavior of radon daughter products in indoor air. Radiation Protection Dosimetry 7 (1984) 107–113.
DOI: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a082973
Google Scholar
[14]
J. Porstendörfer, Properties and behavior of radon and thoron and their decay products in the air, Journal of Aerosol Science 25 (1994) 219–263.
DOI: 10.1016/0021-8502(94)90077-9
Google Scholar
[15]
J. Porstendörfer, Radon: measurements related to dose. Environment International 22 (1996) 563–583.
DOI: 10.1016/s0160-4120(96)00158-4
Google Scholar
[16]
J. Porstendörfer, Physical parameters and dose factors of the radon and thoron decay products. Radiation Protection Dosimetry 94 (2001) 365–373.
DOI: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a006512
Google Scholar
[17]
T.W. Piotr, C.J. Anthony, Unattached fraction measuring technique and radon lung dose, Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 51(1) (2000) 137–151.
DOI: 10.1016/s0265-931x(00)00049-7
Google Scholar
[18]
C. Huet, G. Tymen, D. Boulaud, Size distribution, equilibrium ratio and unattached fraction of radon decay products under typical indoor domestic conditions, The Science of the Total Environment 272 (2001) 97–103.
DOI: 10.1016/s0048-9697(01)00671-4
Google Scholar
[19]
J. Vaupotič, Nano-size radon short-lived progeny aerosols in Slovenian kindergartens in winter time, Chemosphere 69 (2007) 856.
DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.06.022
Google Scholar
[20]
C. Kranrod, S. Tokonami, T. Ishikawa, A. Sorimachi, M. Janik, R. Shingaki, M. Furukawa, S. Chanyotha, N. Chankow, Mitigation of the effective dose of radon decay products through the use of an air cleaner in a dwelling in Okinawa, Japan, Applied Radiation and Isotopes 67 (2009).
DOI: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2009.02.087
Google Scholar
[21]
M. Singh, K. Singh, S. Singh, Z. Papp, Variation of indoor radon progeny concentration and its role in dose assessment. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 99 (2008) 539-545.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2007.08.023
Google Scholar
[22]
M.P. Ruffle, The geometrical efficiency of a parallel disc-source and detector system. Nuclear Instruments and Methods 52 (1967) 354–358.
DOI: 10.1016/0029-554x(67)90248-0
Google Scholar
[23]
A. Wicke, Untersuchungen zur Frage der natu¨ rlichen Radioactivita¨ t der Luft in Wohn un Aufenthaltsraumen. Ph.D. thesis, Univ. Giessen, Germany, (1979).
Google Scholar
[24]
A. Mohammed, Activity size distribution of short-lived radon progeny in indoor air, Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 86(2) (1999) 139–145.
DOI: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.rpd.a032933
Google Scholar
[25]
A. Mohamed, M. Abd El-hady, M. Moustafa, M. Yuness, Deposition pattern of inhaled radon progeny size distribution in human lung. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences. 7(3) (2014) 333-337.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jrras.2014.05.004
Google Scholar
[26]
A. Mohamed, A.A. Ahmed, A.E. Ali, M. Yuness, Attached and unattached activity size distribution of short-lived radon progeny (214pb) and evaluation of deposition fraction, Journal of Nuclear and Radiation Physics, 3 (2008) 101-108.
Google Scholar
[27]
A.M. Marenny, A.S. Vorozhtsov, N.A. Nefedov, O.A. Orlova, Results of radon concentration measurements in some regions of Russia. Radiation Measurements 26 (1996) 43-48.
DOI: 10.1016/1350-4487(94)00090-5
Google Scholar
[28]
M.I. Al-Jarallah, F. Rehman, F. Abu-Jarad, A. Al-Shukri, Indoor radon measurements in dwellings of four Saudi Arabian cities. Radiation Measurements 36 (2003) 445-448.
DOI: 10.1016/s1350-4487(03)00168-9
Google Scholar
[29]
K.M. Abumurad, M.H. Al-Tamimi, Natural radioactivity due to radon in Soum region, Jordan. Radiation Measurements 39 (2005) 77-80.
DOI: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2004.02.017
Google Scholar
[30]
C. Diyun, Y. Xingbao, H. Ruiying, Indoor radon survey in indoor environments in Zhuhai city, China. Radiation Measurements 39 (2005) 205-207.
DOI: 10.1016/j.radmeas.2004.04.012
Google Scholar
[31]
J.C. Ching, C.L. Chi, L. Yu-Ming, Measurement of equilibrium factor and unattached fraction of radon progeny in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. Applied Radiation and Isotopes 49(12) (1998) 1613–1618.
DOI: 10.1016/s0969-8043(98)00065-7
Google Scholar