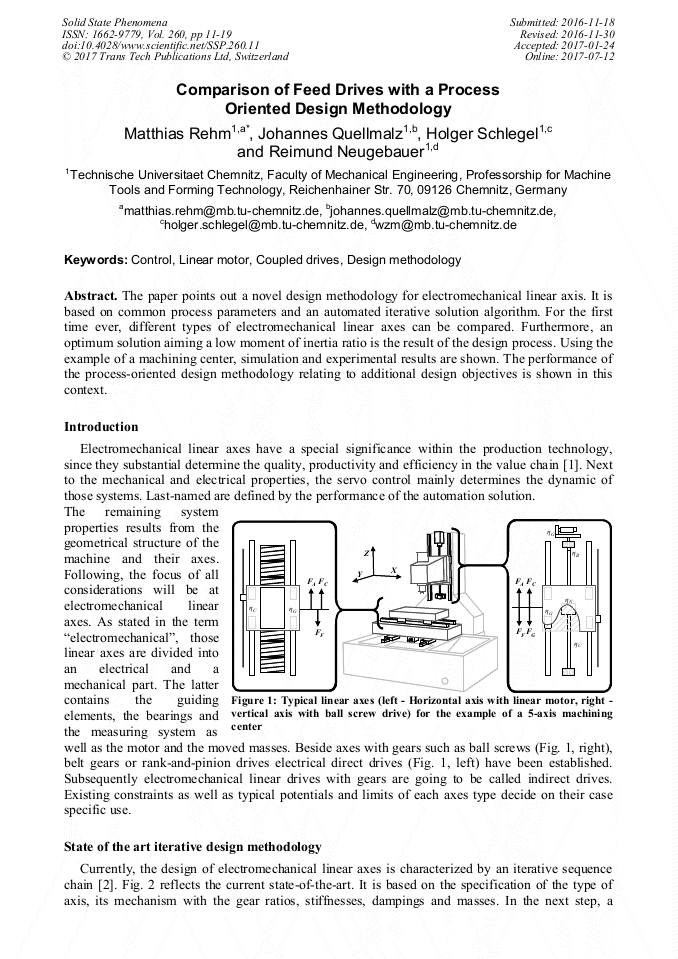
p.3
p.11
p.20
p.33
p.38
p.45
p.51
p.59
Comparison of Feed Drives with a Process Oriented Design Methodology
Abstract:
The paper points out a novel design methodology for electromechanical linear axis. It is based on common process parameters and an automated iterative solution algorithm. For the first time ever, different types of electromechanical linear axes can be compared. Furthermore, an optimum solution aiming a low moment of inertia ratio is the result of the design process. Using the example of a machining center, simulation and experimental results are shown. The performance of the process-oriented design methodology relating to additional design objectives is shown in this context.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
11-19
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
July 2017
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2017 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: