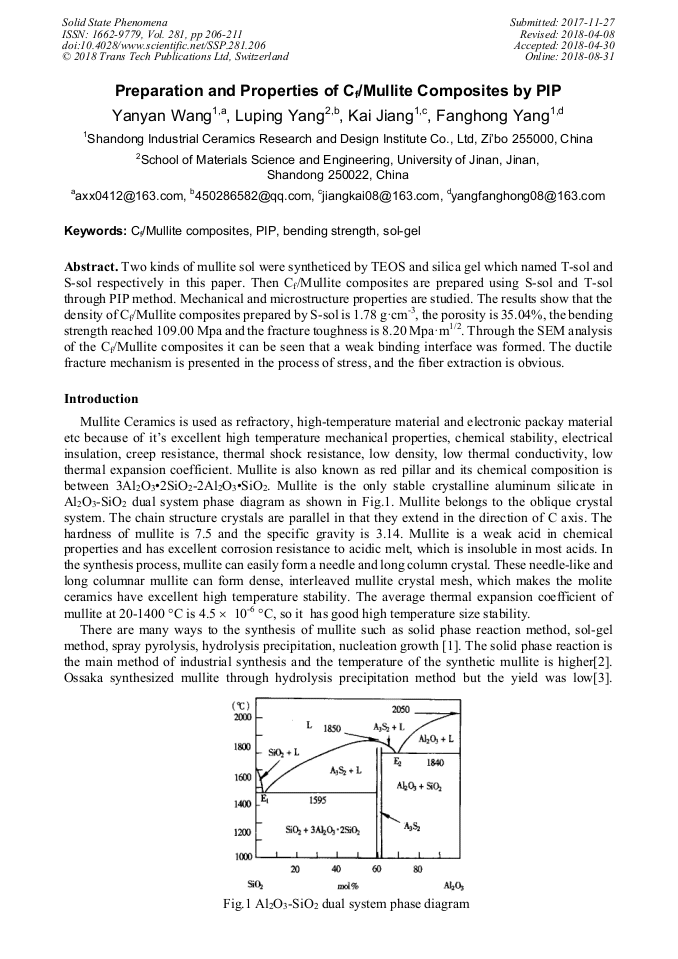
[1]
H. Schneider, D.Voll, B.Saruhan, Synthesis and structural characterization of non-crystalline mullite precursors,Journal of non-crystalline solids. 178(1994)262-271.
DOI: 10.1016/0022-3093(94)90295-x
Google Scholar
[2]
L. B. Kong, Y.Z. Chen, T.S. Zhang, Effect of alkaline-earth oxides on phase for development of mullite ceramics,J. Ceramics International. 30(2004)1319-1323.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2003.12.019
Google Scholar
[3]
J.Ossaka, Tetragonal mullite-like phase from co-precipitated gels,J. Nature. 191(1961) 1000.
DOI: 10.1038/1911000a0
Google Scholar
[4]
M. D. Sacks, N. Bozkurt, G.W. Scheiffele, Fabrication of mullite and mullite-matrix composites by transient viscous sintering of composite powders, J. Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 74(10 (1991)2428-2437.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1991.tb06780.x
Google Scholar
[5]
L. S. Cividanes, T .M. .B Campos, L. A. Rodrigues, Review of mullite synthesis routes by sol-gel method, J. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology. 55(1)(2010) 111-125.
DOI: 10.1007/s10971-010-2222-9
Google Scholar
[6]
D. J. Cassidy, J. L. Woolfrey, J. R. Bartlett, The effect of precursor chemistry on the crystallisation and densification of sol-gel derived mullite gels and powders,J. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology. 10(1)(1997)19-30.
DOI: 10.1023/a:1018328020787
Google Scholar
[7]
B. Bagchi, S. Das, A.Bhattacharya, Effect of nickel and cobalt ions on low temperature synthesis of mullite by sol-gel technique,J. Journal of sol-gel science and technology. 55(2)(2010) 135-141.
DOI: 10.1007/s10971-010-2225-6
Google Scholar
[8]
A. K. Chakravorty, Effect of pH on 980 C spinel phase-mullite formation of Al2O3-SiO2 gels,J. Journal of materials science. 29(6)(1994) 1558-1568.
DOI: 10.1007/bf00368926
Google Scholar
[9]
D. Roy, B. Bagchi, S. Das, Dielectric and magnetic properties of sol-gel derived mullite-iron nanocomposite,J. Journal of electroceramics. 28(4)(2012) 261-267.
DOI: 10.1007/s10832-012-9725-4
Google Scholar
[10]
Bagchi B, Das S, Bhattacharya A, et al. Nanocrystalline mullite synthesis at a low temperature: effect of copper ions[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2009, 92(3): 748-751.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02910.x
Google Scholar
[11]
Zh. L. Wang, P. Xu, Zh. Li, Microstructure and oxidation behavior of sol-gel mullite coating on SiC-coated carbon/carbon composites,J. Journal of the European Ceramic Society. 35(14)(2015) 3789-3796.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2015.06.033
Google Scholar
[12]
Y. Wang, H. Liu, H. Cheng, Densification behavior and microstructure of mullite obtained from diphasic Al2O3SiO2 gels,J. Ceramics International. 40(8)(2014) 12789-12796.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.04.133
Google Scholar
[13]
P. Liu, Y. Zhu, J. Ma, Effect of boehmite sol on the crystallization behavior and densification of mullite formed from a sol-gel precursor,J. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International. 23(2)(2013) 145-151.
DOI: 10.1016/j.pnsc.2013.02.004
Google Scholar
[14]
J. A. Pask, A .P. Tomsia, Formation of Mullite from Sol-Gel Mixtures and Kaolinite,J. Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 74(10)(1991) 2367-73.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1991.tb06770.x
Google Scholar
[15]
M. K. Haldar, Effect of magnesia additions on the properties of zirconia-mullite composites derived from sillimanite beach sand, J. Ceramics international. 29(2003) 573-581.
DOI: 10.1016/s0272-8842(02)00204-3
Google Scholar
[16]
E. Roch-Rangel, S. Díaz-de-la-Torre, M. Umemoto, Zirconia-mullite composites consolidated by spark plasma reaction sintering from zircon and alumina, J. Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 88(2005) 1150-1157.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2005.00234.x
Google Scholar
[17]
H. C. Park, T. Y. Yang, S. Y. Yoon, Preparation of zirconia-mullite composites by an infiltration route, J. Materials Science and Engineering: A. 405(2005) 233-238.
DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2005.06.005
Google Scholar
[18]
J. Y. Yang, J. H. Weaver, F. W. Zok, Processing of Oxide Composites with Three-Dimensional Fiber Architectures, J. Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 92(2009) 1087-1092.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03036.x
Google Scholar