p.327
p.333
p.338
p.344
p.353
p.357
p.362
p.371
p.378
Biomimically Leg-Kinematics on Walking Robots
Abstract:
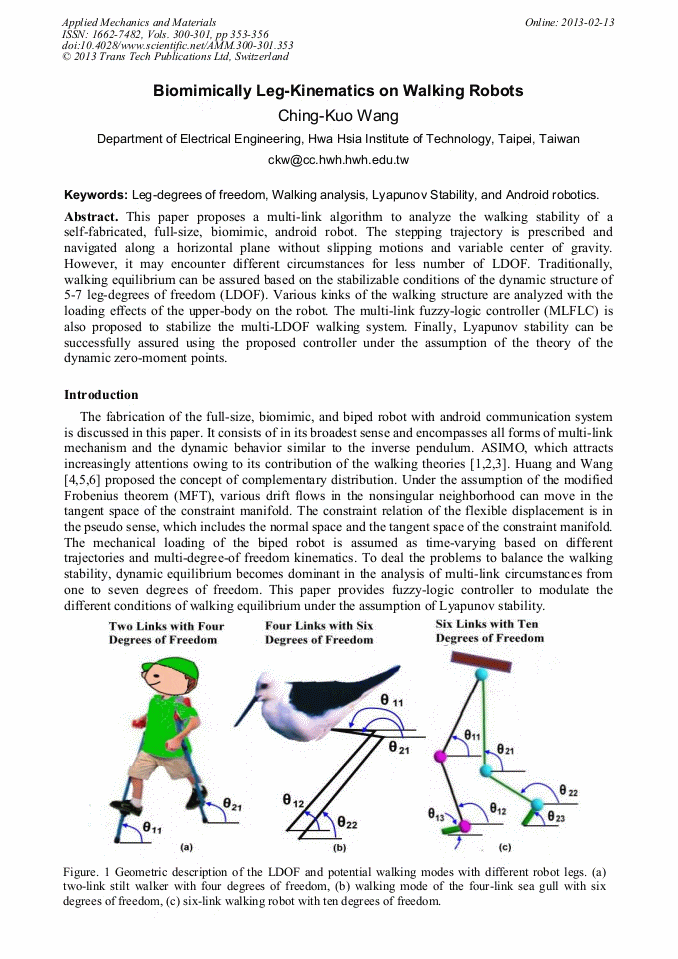
This paper proposes a multi-link algorithm to analyze the walking stability of a self-fabricated, full-size, biomimic, android robot. The stepping trajectory is prescribed and navigated along a horizontal plane without slipping motions and variable center of gravity. However, it may encounter different circumstances for less number of LDOF. Traditionally, walking equilibrium can be assured based on the stabilizable conditions of the dynamic structure of 5-7 leg-degrees of freedom (LDOF). Various kinks of the walking structure are analyzed with the loading effects of the upper-body on the robot. The multi-link fuzzy-logic controller (MLFLC) is also proposed to stabilize the multi-LDOF walking system. Finally, Lyapunov stability can be successfully assured using the proposed controller under the assumption of the theory of the dynamic zero-moment points
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
353-356
Citation:
Online since:
February 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: