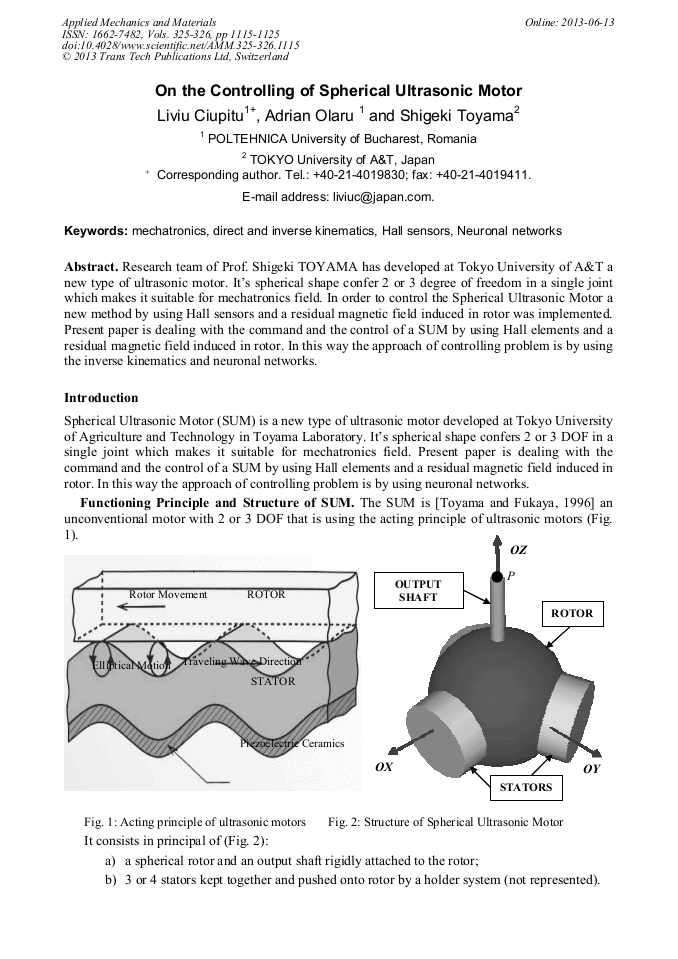
[1]
L. Ciupitu, S. Toyama and E. Purwanto (2002). Development of a Method for Controlling the Spherical Ultrasonic Motor by using Magnetic Field, In: Romanian Journal of Technical Science - Applied Mechanics, special number 2002, tome 47, pp.155-158, Editura Academiei Romane, Bucharest, Romania.
Google Scholar
[2]
L. Ciupitu, S. Toyama and E. Purwanto (2002). Robotic Arm with 9 DOF Driven by Spherical Ultrasonic Motors. In: Borangiu Ed. Proc. of IFAC Symposium "Intelligent Assembly and Disassembly", Bucharest, Romania, 2003, pp.85-90.
DOI: 10.1016/s1474-6670(17)37666-8
Google Scholar
[3]
A. Gray. Modern Differential Geometry. CRE Press, 1998.
Google Scholar
[4]
T. Okuyama, E. Purwanto and S. Toyama. Nethods for Detecting an Arbitrary Orientation of a Spherical Ultrasonic Motor. In: J. Mrazek, et al (eds.). Proc. of IX International Conference on the Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, Liberec, Czech Republic, 2004, pp.573-578.
Google Scholar
[5]
E. Purwanto and S. Toyama. Control Method of a Spherical Ultrasonic Motor, In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronis (AIM 2003), Kobe, Japan, July 2003, vol. 2, pp.1321-1326.
DOI: 10.1109/aim.2003.1225534
Google Scholar
[6]
E. Purwanto, S. Toyama, N. Toyoda and H. Murakami. Control Method of Spherical Ultrasonic Motor with Magnetized Rotor, In: Proceedings of International Conference ICMA'02, Tampere University of Technology, Finland, 2002, pp.387-394.
Google Scholar
[7]
S. Toyama and N. Fukaya. Development of a New Spherical Ultrasonic Motor, . In: D. Fabrizi, Ed. Proceedings of 27-th International Symposium on Industrial Robots "Robotics Toward 2000", 1996, Milano, Italy, pp.453-457.
Google Scholar
[8]
P.J. Alsina, N.S. Gehlot, Direct and inverse kinematics of robot manipulator based on modular neural networks, ICARCV, IEEE, pp.1743-7, 3, 1994.
Google Scholar
[9]
R. Manseur, D.Keith, A fast algorithm for reverse kinematics analysis of robot manipulator, International Journal of Robotics Research, 7 (3), 1998, pp.622-648.
Google Scholar
[10]
D. Gorinevsky, T.Connoly, Comparations of some neural network and scattered data approximations: The inverse manipulator kinematics example, Neural computation, 3 (6), pp.521-542.
DOI: 10.1162/neco.1994.6.3.521
Google Scholar
[11]
L.Lee, Training feedforward neural networks: An algorithm givin improved generalization, Neural Networks, 10 (1), pp.61-68, 1997.
DOI: 10.1016/s0893-6080(96)00071-8
Google Scholar
[12]
C. Schittenkopf, G.Deco and W. Brauner, Two strategies to avoid overfitting in feedforward networks, Neural Networks, 10 (3), pp.505-516, 1997.
DOI: 10.1016/s0893-6080(96)00086-x
Google Scholar
[13]
Olaru, A., Olaru S., Ciupitu, L. Assisted research of the neural network by bach propagation algorithm, OPTIROB 2010 International Conference, Calimanesti, Romania, The RPS Singapore Book, pp.194-200 , 2010.
Google Scholar
[14]
Olaru, A., Olaru, S., Paune D., Ghionea A. Assisted research of the neural network, OPTIROB 2010 International Conference, Calimanesti, Romania, The Research Publishing Services Singapore Book, pp.189-194 , 2010.
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.463-464.1098
Google Scholar
[15]
Olaru, A., Olaru, S. Assisted research of the neural network with LabVIEW instrumentation, IEEE ICMENS-2010 Proceedings, Changsha, China, pp.1-8, 2010.
Google Scholar
[16]
Olaru, A., Oprean, A., Olaru, S., Paune, D. Optimization of the neural network by using the LabVIEW instrumentation, IEEE ICMERA 2010 Proceedings, ISBN 978-1-4244-8867-4, IEEE catalog number CFP1057L-ART, pp.40-44, 2010.
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.463-464.1011
Google Scholar
[17]
Olaru, A., Olaru, S., Paune, D. Assisted research dynamic neural network with time delay and recurrent links, IEEE ICMERA 2010 Proceedings, ISBN 978-1-4244-8867-4, IEEE catalog number CFP1057L-ART, pp.284-288, 2010.
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.463-464.1094
Google Scholar
[18]
M. Minsky and S. Papert, Perceptrons: an introduction to computational geometry, The MIT Press, Cambridge MA, 1969.
Google Scholar
[19]
J. J. Hopfield, "Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities", Proc. of the National Academy of Sciences, 81, 1984, pp.3088-3092.
Google Scholar
[20]
Hajduk, M., Semjon, J., Vagaš, M.: Design of the Welding Fixture for the Robotic Station for Spot Weldind Based on the Modular Concept. In: Acta Mechanica Slovaca No. 3/2009, volume 13, pp.30-35, ISSN 1335-2393.
DOI: 10.2478/v10147-010-0044-y
Google Scholar
[21]
Hajduk, M., Sukop, M., Baláž, V., Semjon, J., Vagaš, M.: Improving the performance of manufacturing systems based reconfiguring and computer integration. Košice, 2006.
Google Scholar
[22]
Páchniková L., Šalátová, M.: Ciele a efekty pružných výrob. In: Acta Mechanica Slovaca, roč. 12, č. 2-A, 2008, pp.451-454, ISSN 1335-2393.
Google Scholar
[23]
Páchniková L.: Profiling production cells based on simulation. In: Modelling and designing in production engineering, Lublin 2009, pp.132-137, ISBN 978-83-87833-91-6.
Google Scholar