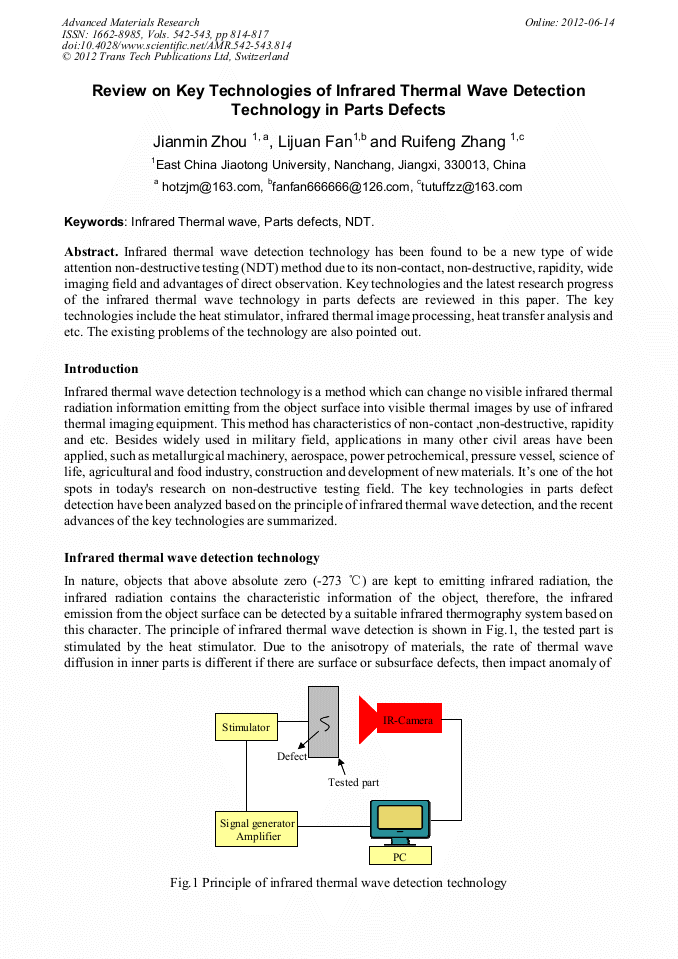
[1]
Xiaolin Yang, Lailin Du and Lichun Feng: Journal of LASER & INFRARED, Vol.37 (11) (2007), p.1188.In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[2]
Zhongchan Lv,Yupeng Tian and Keyin Zhou: NDT Vol.29(6) (2005), p.44. In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[3]
Xiaolin Yang,Boping Lv and Mingle Xian: NDT Vol.30(6) (2008), p.369.In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[4]
J. Wilson, G.Y. Tian and I.Z. Abidin,et al.Pulsed Eddy Current Thermography: System Development and Evaluation. Insight—Non-Destructive Testing and Condition Monitoring, Vol.52(2) (2010), p.87.
DOI: 10.1784/insi.2010.52.2.87
Google Scholar
[5]
Chunfei Xing,Yanhong Li and Dapeng Chen: Journal of Applied Optics Vol.30(3) (2009), p.465. In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[6]
Youfu Ding,Xiaochuan Zhang and Xiaolin Yang: NDT, Vol.28(12) (2006), p.620. In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[7]
Yupeng Tian. Research on Key Technologies of Infrared Thermography [D]. Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,(2009). In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[8]
Yu Chen. Infrared Millim. Waves.Vol.19(4) (2008) , p.285. In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[9]
Xiangqiao Yan and Haipeng Wu: Journal of harbin institute of techonology.Vol.35(4) (2003), p.405. In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[10]
Shuwen Xue and Weiming Hong: Journal of zhanjiang normal college. Vol. 26(3) (2005), p.24. In Chinese.
Google Scholar
[11]
Shapard S, Lhota J and Rubadeux B, et al. Reconstruction and enhancement of active thermographic image sequences. Opt. Eng. Vol.42(5)(2003), p.1337.
DOI: 10.1117/1.1566969
Google Scholar
[12]
X. Maldague and Marinetti. S. J. Appl. Phys. Vol.79(5) (1996), p.2694.
Google Scholar
[13]
N. Rajic. Principal component thermography for flaw contrast enhancement and flaw depth characterisation in composite structures .Composite Structures. Vol.58(2002), p.521.
DOI: 10.1016/s0263-8223(02)00161-7
Google Scholar
[14]
Marinetti S., Grinzato E.and Bison P.G, et al. Statistical analysis of IR thermographic sequences by PCA. Infrared Phys. & Technol. Vol.46(2005), p.85.
DOI: 10.1016/j.infrared.2004.03.012
Google Scholar
[15]
Xingwang Guo,Gongchen Gao and Zhenxia Lv. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics.Vol.32(8) (2006), p.937. In Chinese.
Google Scholar