p.990
p.996
p.1002
p.1007
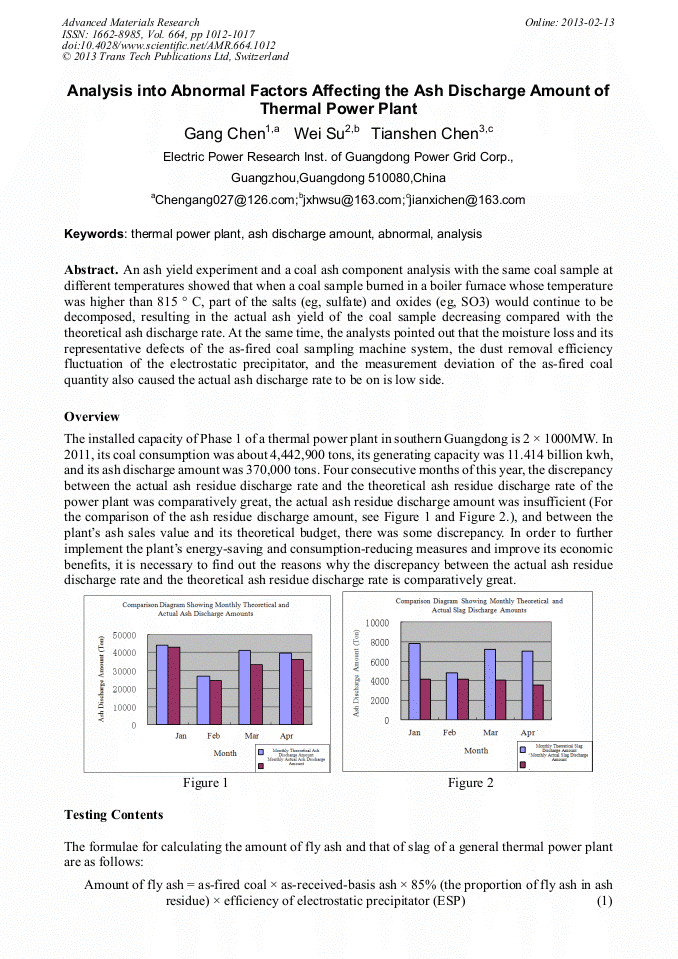
p.1012
p.1021
p.1028
p.1035
p.1041
Analysis into Abnormal Factors Affecting the Ash Discharge Amount of Thermal Power Plant
Abstract:
An ash yield experiment and a coal ash component analysis with the same coal sample at different temperatures showed that when a coal sample burned in a boiler furnace whose temperature was higher than 815 ° C, part of the salts (eg, sulfate) and oxides (eg, SO3) would continue to be decomposed, resulting in the actual ash yield of the coal sample decreasing compared with the theoretical ash discharge rate. At the same time, the analysts pointed out that the moisture loss and its representative defects of the as-fired coal sampling machine system, the dust removal efficiency fluctuation of the electrostatic precipitator, and the measurement deviation of the as-fired coal quantity also caused the actual ash discharge rate to be on is low side.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1012-1017
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
February 2013
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: