p.636
p.645
p.655
p.663
p.671
p.677
p.687
p.695
p.699
Virtual Composite Manufacturing Simulation Chain
Abstract:
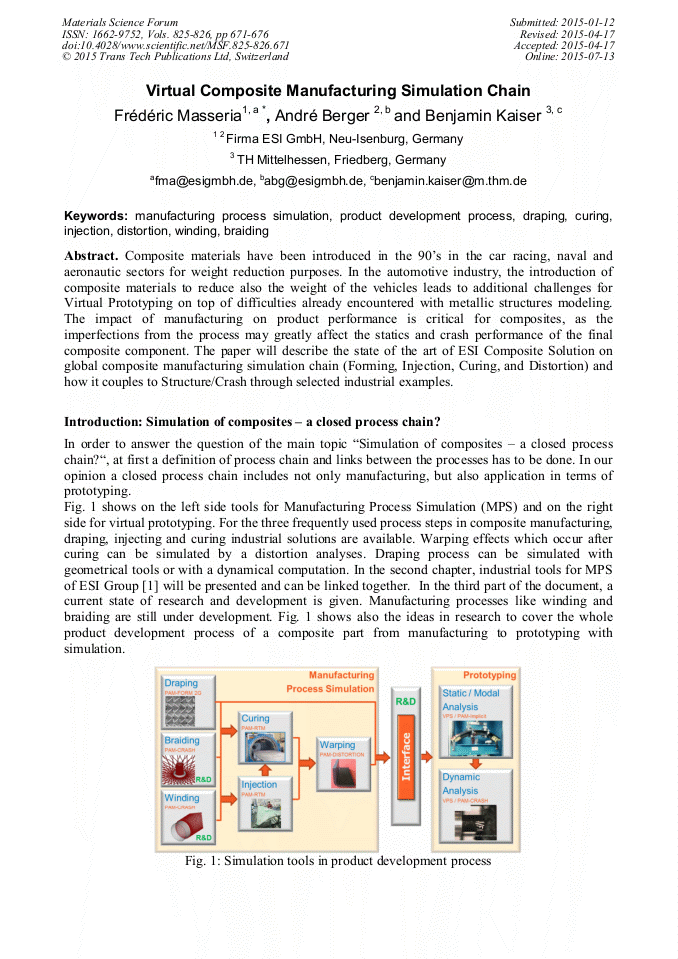
Composite materials have been introduced in the 90’s in the car racing, naval and aeronautic sectors for weight reduction purposes. In the automotive industry, the introduction of composite materials to reduce also the weight of the vehicles leads to additional challenges for Virtual Prototyping on top of difficulties already encountered with metallic structures modeling. The impact of manufacturing on product performance is critical for composites, as the imperfections from the process may greatly affect the statics and crash performance of the final composite component. The paper will describe the state of the art of ESI Composite Solution on global composite manufacturing simulation chain (Forming, Injection, Curing, and Distortion) and how it couples to Structure/Crash through selected industrial examples.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
671-676
Citation:
Online since:
July 2015
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2015 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: