p.483
p.489
p.495
p.500
p.507
p.513
p.517
p.521
p.526
Electrochromic Glazings for Window Applications
Abstract:
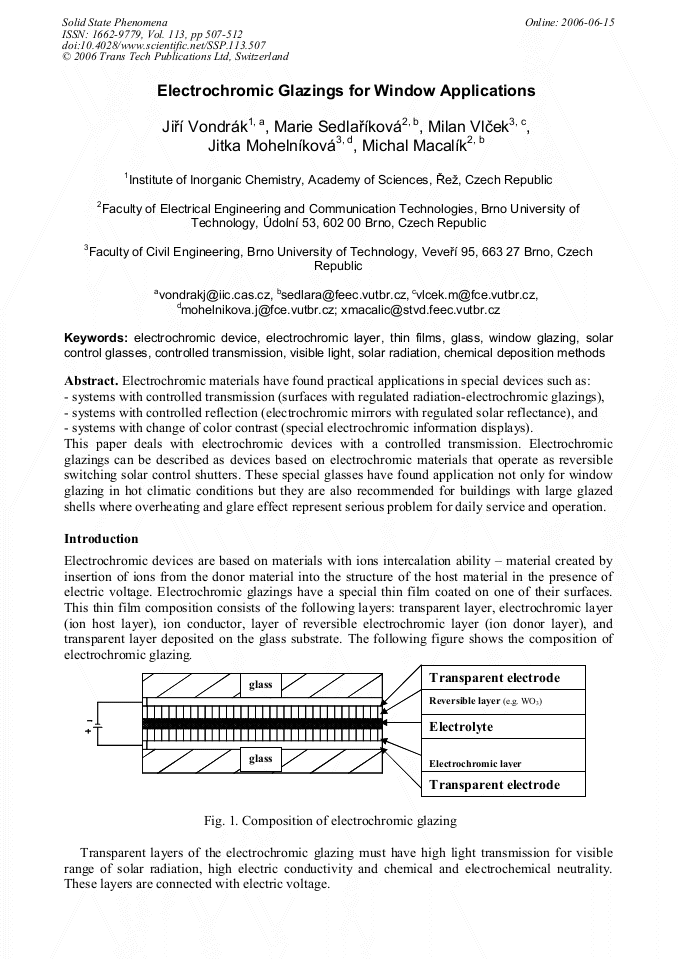
Electrochromic materials have found practical applications in special devices such as: - systems with controlled transmission (surfaces with regulated radiation-electrochromic glazings), - systems with controlled reflection (electrochromic mirrors with regulated solar reflectance), and - systems with change of color contrast (special electrochromic information displays). This paper deals with electrochromic devices with a controlled transmission. Electrochromic glazings can be described as devices based on electrochromic materials that operate as reversible switching solar control shutters. These special glasses have found application not only for window glazing in hot climatic conditions but they are also recommended for buildings with large glazed shells where overheating and glare effect represent serious problem for daily service and operation.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
507-512
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
June 2006
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2006 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: