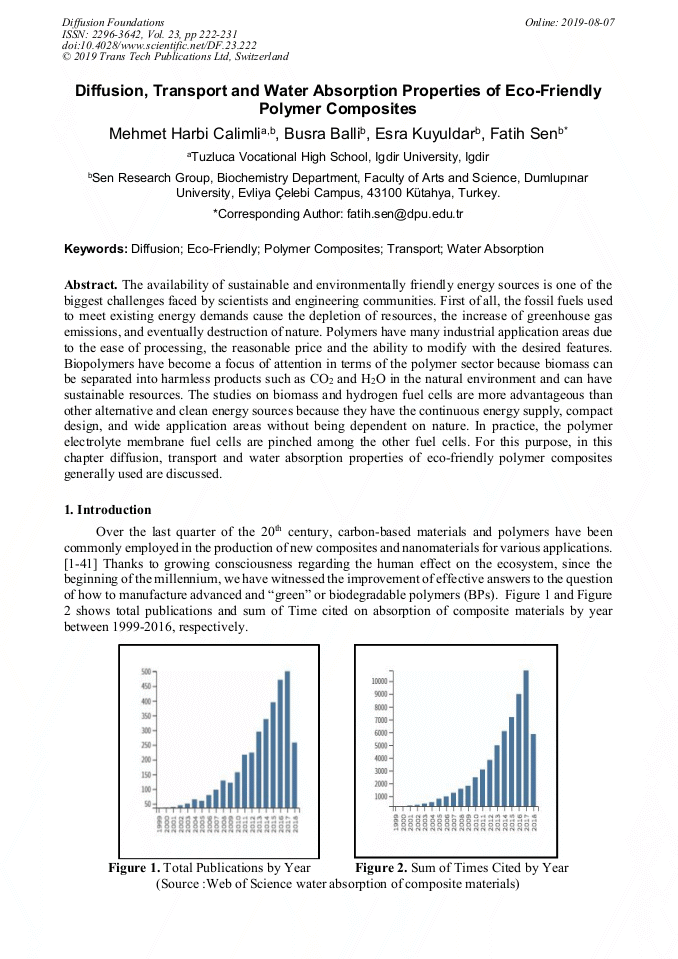
[1]
B. Aday, Y. Yıldız, R. Ulus, S. Eris, F. Sen, M. Kaya, One-Pot, Efficient and Green Synthesis of Acridinedione Derivatives Using Highly Monodisperse Platinum Nanoparticles Supported with Reduced Graphene Oxide, New J. Chem. 40 (2016) 748–754.
DOI: 10.1039/c5nj02098k
Google Scholar
[2]
B. Aday, H. Pamuk, M. Kaya, F. Sen, Graphene Oxide as Highly Effective and Readily Recyclable Catalyst Using for the One-Pot Synthesis of 1,8-Dioxoacridine Derivatives, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 16 (2016) 6498–6504.
DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2016.12432
Google Scholar
[3]
B. Sen, A. Şavk, E. Kuyuldar, S. Karahan Gülbay, F. Sen, Hydrogen Liberation from The Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Hydrazine Borane in Acidic Media, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43 (2018) 17978–17983.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.03.225
Google Scholar
[4]
B. Şen, B. Demirkan, A. Şavk, S. Karahan Gülbay, F. Şen, Trimetallic PdRuNi Nanocomposites Decorated on Graphene Oxide: A Superior Catalyst for The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43 (2018) 17984–17992.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.07.122
Google Scholar
[5]
B. Şen, B. Demirkan, M. Levent, A. Şavk, F. Şen, Silica-based Monodisperse PdCo Nanohybrids as Highly Efficient and Stable Nanocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43 (2018) 20234–20242.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.07.080
Google Scholar
[6]
B. Şen, B. Demirkan, A. Savk, R. Kartop, M.S. Nas, M.H. Alma, S. Sürdem, F. Şen, High-performance graphite-supported ruthenium nanocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction, J. Mol. Liq. 268 (2018) 807–812.
DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.07.117
Google Scholar
[7]
A. Savk, B. Özdil, B. Demirkan, M.S. Nas, M.H. Calimli, M.H. Alma, Inamuddin, A.M. Asiri, F. Şen, Multiwalled carbon nanotube-based nanosensor for ultrasensitive detection of uric acid, dopamine, and ascorbic acid, Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 99 (2019) 248–254.
DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.113
Google Scholar
[8]
B. Sen, E. Kuyuldar, A. Şavk, H. Calimli, S. Duman, F. Sen, Monodisperse ruthenium copper alloy nanoparticles decorated on reduced graphene oxide for dehydrogenation of DMAB, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 44 (2019) 10744–10751.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.02.176
Google Scholar
[9]
R. Ayranci, B. Demirkan, B. Sen, A. Şavk, M. Ak, F. Şen, Use of the monodisperse Pt/Ni@rGO nanocomposite synthesized by ultrasonic hydroxide assisted reduction method in electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose detection, Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 99 (2019) 951–956.
DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.02.040
Google Scholar
[10]
S. Taçyıldız, B. Demirkan, Y. Karataş, M. Gulcan, F. Sen, Monodisperse Ru Rh bimetallic nanocatalyst as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolytic dehydrogenation of methylamine-borane, J. Mol. Liq. 285 (2019) 1–8.
DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2019.04.019
Google Scholar
[11]
Z. Daşdelen, Y. Yıldız, S. Eriş, F. Şen, Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Pt Nanoparticles Decorated on GO-PVP Hybride Material for Methanol Oxidation Reaction, Appl. Catal. B Environ. 219 (2017) 511–516.
DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.08.014
Google Scholar
[12]
T. Demirci, B. Çelik, Y. Yıldız, S. Eriş, M. Arslan, F. Sen, B. Kilbas, One-pot synthesis of Hantzsch dihydropyridines using a highly efficient and stable PdRuNi@GO catalyst, RSC Adv. 6 (2016) 76948–76956.
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra13142e
Google Scholar
[13]
S. Akocak, B. Şen, N. Lolak, A. Şavk, M. Koca, S. Kuzu, F. Şen, One-Pot Three-Component Synthesis of 2-Amino-4H-Chromene Derivatives by Using Monodisperse Pd Nanomaterials Anchored Graphene Oxide as Highly Efficient and Recyclable Catalyst, Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects. 11 (2017) 25–31.
DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoso.2017.06.002
Google Scholar
[14]
E. Demir, A. Savk, B. Sen, F. Sen, A Novel Monodisperse Metal Nanoparticles Anchored Graphene Oxide as Counter Electrode for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells, Nano-Structures and Nano-Objects. 12 (2017) 41–45.
DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoso.2017.08.018
Google Scholar
[15]
E. Demir, B. Sen, F. Sen, Highly Efficient Pt Nanoparticles and f-MWCNT Nanocomposites Based Counter Electrodes for Dye-sensitized Solar Cells, Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects. 11 (2017) 39–45.
DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoso.2017.06.003
Google Scholar
[16]
E. Erken, H. Pamuk, Ö. Karatepe, G. Başkaya, H. Sert, O.M. Kalfa, F. Şen, New Pt(0) Nanoparticles as Highly Active and Reusable Catalysts in the C1–C3 Alcohol Oxidation and the Room Temperature Dehydrocoupling of Dimethylamine-Borane (DMAB), J. Clust. Sci. 27 (2016) 9–23.
DOI: 10.1007/s10876-015-0892-8
Google Scholar
[17]
E. Erken, Y. Yıldız, B. Kilbaş, F. Şen, Synthesis and Characterization of Nearly Monodisperse Pt Nanoparticles for C 1 to C 3 Alcohol Oxidation and Dehydrogenation of Dimethylamine-borane (DMAB), J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 16 (2016) 5944–5950.
DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2016.11683
Google Scholar
[18]
E. Erken, İ. Esirden, M. Kaya, F. Sen, A rapid and novel method for the synthesis of 5-substituted 1H-tetrazole catalyzed by exceptional reusable monodisperse Pt NPs@AC under the microwave irradiation, RSC Adv. 5 (2015) 68558–68564.
DOI: 10.1039/c5ra11426h
Google Scholar
[19]
S. Eris, Z. Daşdelen, F. Sen, Investigation of electrocatalytic activity and stability of Pt@f-VC catalyst prepared by in-situ synthesis for Methanol electrooxidation, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43 (2018) 385–390.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.11.063
Google Scholar
[20]
S. Eris, Z. Daşdelen, Y. Yıldız, F. Sen, Nanostructured Polyaniline-rGO Decorated Platinum Catalyst with Enhanced Activity and Durability for Methanol Oxidation, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43 (2018) 1337–1343.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.11.051
Google Scholar
[21]
İ. Esirden, E. Erken, M. Kaya, F. Sen, Monodisperse Pt NPs@rGO as Highly Efficient and Reusable Heterogeneous Catalysts for The Synthesis of 5-Substituted 1H-Tetrazole Derivatives, Catal. Sci. Technol. 5 (2015) 4452–4457.
DOI: 10.1039/c5cy00864f
Google Scholar
[22]
H. Göksu, Y. Yıldız, B. Çelik, M. Yazıcı, B. Kılbaş, F. Şen, Highly Efficient and Monodisperse Graphene Oxide Furnished Ru/Pd Nanoparticles for the Dehalogenation of Aryl Halides via Ammonia Borane, ChemistrySelect. 1 (2016) 953–958.
DOI: 10.1002/slct.201600207
Google Scholar
[23]
S. Bozkurt, B. Tosun, B. Sen, S. Akocak, A. Savk, M.F. Ebeoğlugil, F. Sen, A Hydrogen Peroxide Sensor Based on TNM Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide Grafted with Highly Monodisperse Pd Nanoparticles, Anal. Chim. Acta. 989 (2017) 88–94.
DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.07.051
Google Scholar
[24]
H. Göksu, S.F. Ho, Ö. Metin, K. Korkmaz, A. Mendoza Garcia, M.S. Gültekin, S. Sun, Tandem Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane and Hydrogenation of Nitro/Nitrile Compounds Catalyzed by Graphene-Supported NiPd Alloy Nanoparticles, ACS Catal. 4 (2014) 1777–1782.
DOI: 10.1021/cs500167k
Google Scholar
[25]
H. Goksu, Y. Yıldız, B. Çelik, M. Yazici, B. Kilbas, F. Sen, Eco-friendly Hydrogenation of Aromatic Aldehyde Compounds by Tandem Dehydrogenation of Dimethylamine-Borane in The Presence of A Reduced Graphene Oxide Furnished Platinum Nanocatalyst, Catal. Sci. Technol. 6 (2016) 2318–2324.
DOI: 10.1039/c5cy01462j
Google Scholar
[26]
Ö. Karatepe, Y. Yıldız, H. Pamuk, S. Eris, Z. Dasdelen, F. Sen, Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Highly Monodisperse Pt@PPy–PANI Nanocomposites as A Novel Catalyst for The Electro-Oxidation of Methanol., RSC Adv. 6 (2016) 50851–50857.
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra06210e
Google Scholar
[27]
B. Şahin, A. Aygün, H. Gündüz, K. Şahin, E. Demir, S. Akocak, F. Şen, Cytotoxic Effects of Platinum Nanoparticles Obtained from Pomegranate Extract by The Green Synthesis Method on The MCF-7 Cell Line, Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces. 163 (2018) 119–124.
DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.12.042
Google Scholar
[28]
B. Şahin, E. Demir, A. Aygün, H. Gündüz, F. Şen, Investigation of the effect of pomegranate extract and monodisperse silver nanoparticle combination on MCF-7 cell line, J. Biotechnol. 260 (2017) 79–83.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.09.012
Google Scholar
[29]
R. Ulus, Y. Yıldız, S. Eriş, B. Aday, F. Şen, M. Kaya, Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (f-MWCNT) as Highly Efficient and Reusable Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Synthesis of Acridinedione Derivatives, ChemistrySelect. 1 (2016) 3861–3865.
DOI: 10.1002/slct.201600719
Google Scholar
[30]
Y. Yıldız, E. Erken, H. Pamuk, H. Sert, F. Şen, Monodisperse Pt Nanoparticles Assembled on Reduced Graphene Oxide: Highly Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for Methanol Oxidation and Dehydrocoupling of Dimethylamine-Borane (DMAB), J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 16 (2016) 5951–5958.
DOI: 10.1166/jnn.2016.11710
Google Scholar
[31]
Y. Yıldız, H. Pamuk, Ö. Karatepe, Z. Dasdelen, F. Sen, Carbon Black Hybrid Material Furnished Monodisperse Platinum Nanoparticles as Highly Efficient and Reusable Electrocatalysts for Formic Acid Electro-oxidation, RSC Adv. 6 (2016) 32858–32862.
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra00232c
Google Scholar
[32]
Y. Yıldız, S. Kuzu, B. Sen, A. Savk, S. Akocak, F. Şen, Different ligand based monodispersed Pt nanoparticles decorated with rGO as highly active and reusable catalysts for the methanol oxidation, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 42 (2017) 13061–13069.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.03.230
Google Scholar
[33]
Y. Koskun, A. Şavk, B. Şen, F. Şen, Highly Sensitive Glucose Sensor Based on Monodisperse Palladium Nickel/Activated Carbon Nanocomposites, Anal. Chim. Acta. 1010 (2018) 37–43.
DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.01.035
Google Scholar
[34]
B. Çelik, E. Erken, S. Eriş, Y. Yıldız, B. Şahin, H. Pamuk, F. Sen, Highly monodisperse Pt(0)@AC NPs as highly efficient and reusable catalysts: the effect of the surfactant on their catalytic activities in room temperature dehydrocoupling of DMAB, Catal. Sci. Technol. 6 (2016) 1685–1692.
DOI: 10.1039/c5cy01371b
Google Scholar
[35]
B. Şen, A. Aygün, A. Şavk, S. Akocak, F. Şen, Bimetallic Palladium–iridium Alloy Nanoparticles as Highly Efficient and Stable Catalyst for The Hydrogen Evolution Reaction, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43 (2018) 20183–20191.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.07.081
Google Scholar
[36]
B. Şen, A. Aygün, T.O. Okyay, A. Şavk, R. Kartop, F. Şen, Monodisperse Palladium Nanoparticles Assembled on Graphene Oxide with The High Catalytic Activity and Reusability in The Dehydrogenation of Dimethylamine-borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 43 (2018) 20176–20182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ij, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 43 (2018) 20176–20182.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.03.175
Google Scholar
[37]
B. Çelik, Y. Yıldız, H. Sert, E. Erken, Y. Koşkun, F. Şen, Monodispersed palladium–cobalt alloy nanoparticles assembled on poly(N-vinyl-pyrrolidone) (PVP) as a highly effective catalyst for dimethylamine borane (DMAB) dehydrocoupling, RSC Adv. 6 (2016) 24097–24102.
DOI: 10.1039/c6ra00536e
Google Scholar
[38]
B. Çelik, S. Kuzu, E. Erken, H. Sert, Y.Y. Koşkun, F. Şen, Nearly Monodisperse Carbon Nanotube Furnished Nanocatalysts as Highly Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for Dehydrocoupling of DMAB and C1 to C3 Alcohol Oxidation, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 41 (2016) 3093–3101.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.12.138
Google Scholar
[39]
B. Sen, S. Kuzu, E. Demir, S. Akocak, F. Sen, Highly monodisperse RuCo nanoparticles decorated on functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube with the highest observed catalytic activity in the dehydrogenation of dimethylamine−borane, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 42 (2017) 23292–23298.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.06.032
Google Scholar
[40]
B. Çelik, G. Başkaya, H. Sert, Ö. Karatepe, E. Erken, F. Şen, B. Celik, G. Baskaya, H. Sert, O. Karatepe, E. Erken, F. Sen, Monodisperse Pt(0)/DPA@GO nanoparticles as highly active catalysts for alcohol oxidation and dehydrogenation of DMAB, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 41 (2016) 5661–5669.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.02.061
Google Scholar
[41]
B. Sen, E. Kuyuldar, B. Demirkan, T. Onal Okyay, A. Şavk, F. Sen, Highly Efficient Polymer Supported Monodisperse Ruthenium-nickel Nanocomposites for Dehydrocoupling of Dimethylamine Borane, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 526 (2018) 480–486.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.05.021
Google Scholar
[42]
J. Ahmed, S.K. Varshney, Polylactides—Chemistry, Properties and Green Packaging Technology: A Review, Int. J. Food Prop. 14 (2011) 37–58.
DOI: 10.1080/10942910903125284
Google Scholar
[43]
† Suprakas Sinha Ray, ‡ Kazunobu Yamada, *,† Masami Okamoto, ‡ and Akinobu Ogami, K. Ueda‡, New Polylactide/Layered Silicate Nanocomposites. 3. High-Performance Biodegradable Materials, (2003).
DOI: 10.1021/cm020953r
Google Scholar
[44]
S. Sinha Ray, Polylactide-Based Bionanocomposites: A Promising Class of Hybrid Materials, Acc. Chem. Res. 45 (2012) 1710–1720.
DOI: 10.1021/ar3000376
Google Scholar
[45]
T. Amnuaikit, CHAPTER 27. Diffusion and Transport of Liquids, Vapours and Gases Through Natural Rubber Composites and Nanocomposites, in: 2013: p.772–799.
DOI: 10.1039/9781849737654-00772
Google Scholar
[46]
C.A. Kumins, T.K. Kwei, Free volume and other theories, in: Diffus. Polym., (1968).
Google Scholar
[47]
H. Cong, M. Radosz, B. Towler, Y. Shen, Polymer–inorganic nanocomposite membranes for gas separation, Sep. Purif. Technol. 55 (2007) 281–291.
DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2006.12.017
Google Scholar
[48]
C. Nah, M.A. Kader, Barrier Properties of Rubber Nanocomposites, (n.d.) 499–526.
Google Scholar
[49]
A. Jacob, P. Kurian, A.S. Aprem, Transport properties of natural rubber latex layered clay nanocomposites, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 108 (2008) 2623–2629.
DOI: 10.1002/app.26615
Google Scholar
[50]
K. Bhattacharyya, B.S. Goldschmidt, M. Hannink, S. Alexander, A. Jurkevic, J.A. Viator, Gold Nanoparticle–Mediated Detection of Circulating Cancer Cells, Clin. Lab. Med. 32 (2012) 89–101.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cll.2012.01.001
Google Scholar
[51]
W. He, G. Lin, T. Van Nguyen, Diagnostic tool to detect electrode flooding in proton-exchange-membrane fuel cells, AIChE J. 49 (2003) 3221–3228.
DOI: 10.1002/aic.690491221
Google Scholar
[52]
R.M. Barrer, G. Skirrow, Transport and equilibrium phenomena in gas–elastomer systems. I. Kinetic phenomena, J. Polym. Sci. 3 (1948) 549–563.
DOI: 10.1002/pol.1948.120030410
Google Scholar
[53]
C.M. Hussain, Handbook of nanomaterials for industrial applications, n.d. https://books.google.com.tr/books?id=6TtmDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA984&lpg=PA984&dq=%5B17%5D.+M.+Krissanasaeranee,+S.+Wongkasemjit,+A.K.+Cheetham,+D.+Eder,+Chem.+Phys.+Lett.+496+(2010)+133&source=bl&ots=Aw5HNItjIc&sig=ACfU3U34ZDVLa_YWenmgLnFBc1dbGGrbeQ&hl=tr&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwig84fL_fngAhVGqxoKHbXFAMoQ6AEwAXoECAgQAQ#v=onepage&q=%5B17%5D. M. Krissanasaeranee%2C S. Wongkasemjit%2C A.K. Cheetham%2C D. Eder%2C Chem. Phys. Lett. 496 (2010) 133&f=false (accessed March 11, 2019).
DOI: 10.1016/j.cplett.2010.07.043
Google Scholar
[54]
G. Mittal, K.Y. Rhee, V. Mišković-Stanković, D. Hui, Reinforcements in multi-scale polymer composites: Processing, properties, and applications, Compos. Part B Eng. 138 (2018) 122–139.
DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.11.028
Google Scholar
[55]
K. Shirvanimoghaddam, S.U. Hamim, M. Karbalaei Akbari, S.M. Fakhrhoseini, H. Khayyam, A.H. Pakseresht, E. Ghasali, M. Zabet, K.S. Munir, S. Jia, J.P. Davim, M. Naebe, Carbon fiber reinforced metal matrix composites: Fabrication processes and properties, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 92 (2017) 70–96.
DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.10.032
Google Scholar
[56]
A.R. Pereira, J.C.P. de Souza, R.M. Iost, F.C.P.F. Sales, F.N. Crespilho, Application of carbon fibers to flexible enzyme electrodes, J. Electroanal. Chem. 780 (2016) 396–406.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.01.004
Google Scholar
[57]
E. Antolini, Composite materials for polymer electrolyte membrane microbial fuel cells, Biosens. Bioelectron. 69 (2015) 54–70.
DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.02.013
Google Scholar
[58]
A. Malinauskas, J. Malinauskiene, A. Ramanavičius, Conducting polymer-based nanostructurized materials: electrochemical aspects, Nanotechnology. 16 (2005) R51–R62.
DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/r01
Google Scholar