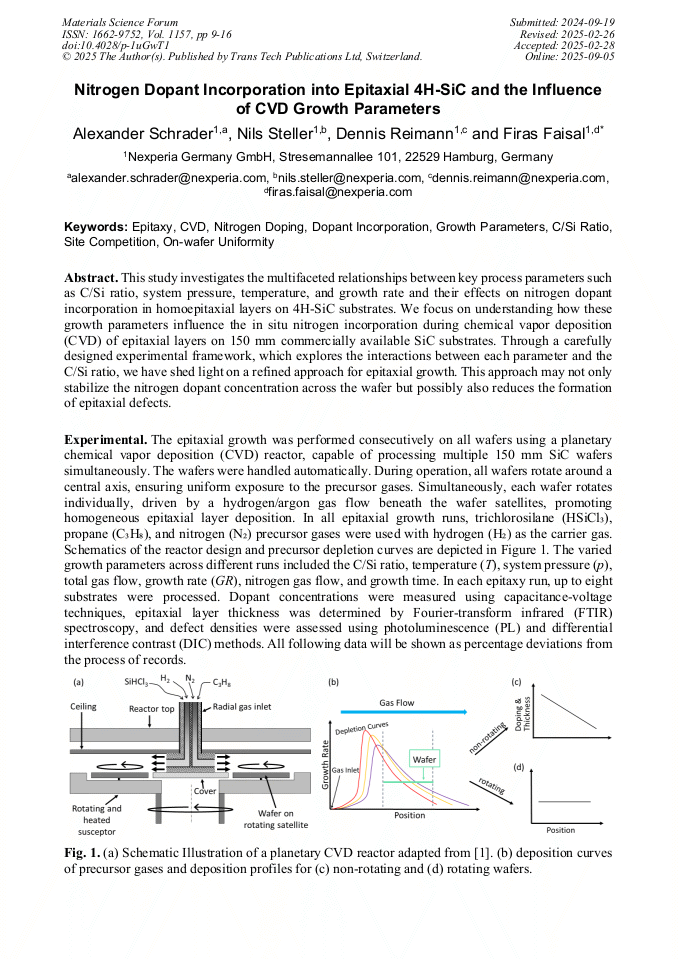
[1]
F. Yang, Modern Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) Reactors and Growing Nitride-based Materials, in Nitride Semiconductor Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs), Elsevier, 2014, p.27–65.
DOI: 10.1533/9780857099303.1.27
Google Scholar
[2]
G. Ferro and D. Chaussende, A New Model for in situ Nitrogen Incorporation into 4H-SiC during Epitaxy, Scientific Reports 7 (2017) 43 069.
DOI: 10.1038/srep43069
Google Scholar
[3]
G. Ferro and D. Chaussende, Revisiting the Site-Competition Doping of 4H-SiC: Cases of N and Al, Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publ Ltd 1004 (2020) 96–101.
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.1004.96
Google Scholar
[4]
U. Forsberg, O. Danielsson, A. Henry, E. Janzen, Nitrogen Doping of Epitaxial Silicon Carbide, Journal of Crystal Growth 236 (2002) 101–112.
DOI: 10.1016/s0022-0248(01)02198-4
Google Scholar
[5]
H. Saitoh, A. Manabe, T. Kimoto, Epitaxial Growth of 4H-SiC {0001} with Large Off-Angles by Chemical Vapor Deposition, Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publ Ltd 527–529 (2006) 223–226.
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.527-529.223
Google Scholar
[6]
M. Zielinski, R. Arvinte, H. Peyre, p-type Doping of 4H- and 3C-SiC Epitaxial Layers with Aluminum, Materials Science Forum, Trans Tech Publ Ltd 858 (2016) 137–142.
DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.858.137
Google Scholar
[7]
J. Zhang, A. Ellison, A. Henry, E. Janzén, Nitrogen Incorporation during 4H-SiC Epitaxy in a Chimney CVD Reactor, Journal of Crystal Growth 226 (2001) 267–276.
DOI: 10.1016/s0022-0248(01)01369-0
Google Scholar
[8]
D. J. Larkin, P. G. Neudeck, L. G. Matus, Site-Competition Epitaxy for Superior Silicon Carbide Electronics, Applied Physics Letters 65 (1994) 1659–1661.
DOI: 10.1063/1.112947
Google Scholar
[9]
Ö. Danielsson, U. Forsberg, E. Janzén, Predicted Nitrogen Doping Concentrations in Silicon Carbide Epitaxial Layers Grown by Hotwall Chemical Vapor Deposition, Journal of Crystal Growth 250 (2003) 471–478.
DOI: 10.1016/s0022-0248(02)02513-7
Google Scholar
[10]
J. Olander, K. M. E. Larsson, Adsorption of N-containing Species onto SiC(0001) Surfaces: A Theoretical Study, Physical Review B - Condensed Matter and Materials Physics 67 (2003) 115306.
DOI: 10.1103/physrevb.67.115306
Google Scholar