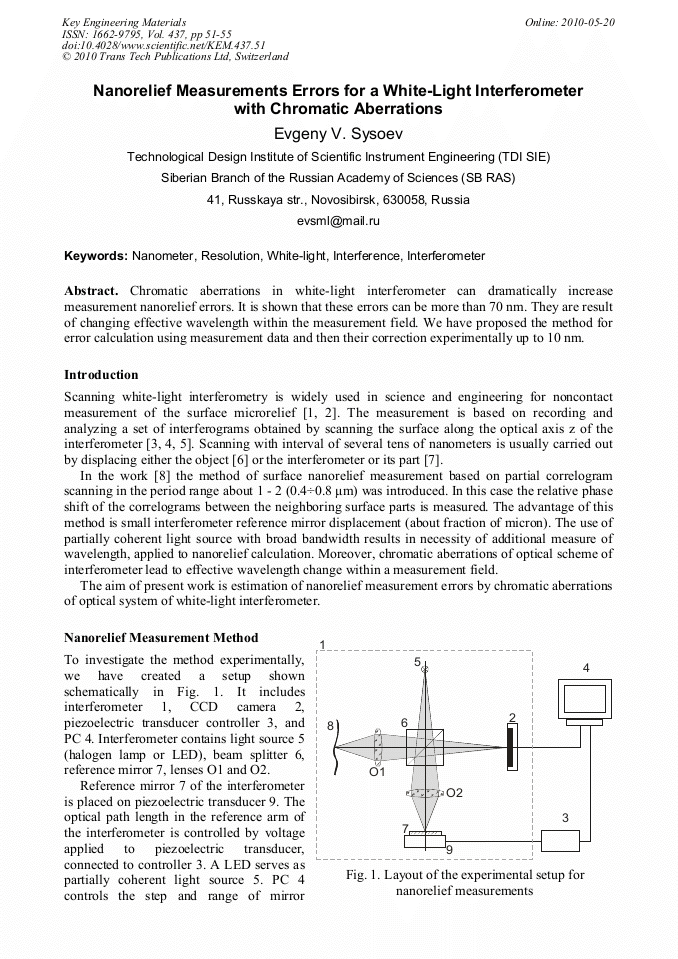
[1]
P. de Groot, J. Biegen, J. Clack, X.C. de Lega, and D. Grigg: Optical interferometry for measurement of the geometric dimensions of industrial parts. Appl. Opt., 19 (2002), pp.3853-3860.
DOI: 10.1364/ao.41.003853
Google Scholar
[2]
M. Davidson, K. Kaufman, and I. Mazor: The coherence probe microscope. Solid State Technol., 30 (1987), pp.57-59.
Google Scholar
[3]
P.J. Caber, S.J. Martinek, R.J. Niemann: A new interferometric profiler for smooth and rough surface. Laser Dimensional Metrology Recent Advances for Industrial Application. M.J. Downs, ed. Proc. SPIE, Vol. 2088 (1993), pp.195-203.
DOI: 10.1117/12.168073
Google Scholar
[4]
David J. Aziz: Interferometric measurement of surface roughness in engine cylinder walls. Opt. Eng., 37 (1998), pp.1429-1434.
DOI: 10.1117/1.601703
Google Scholar
[5]
P. de Groot, X.C. de Lega, J. Kramer, and M. Turzhitsky: Determination of fringe order in white-light interference microscopy. Appl. Opt., 22 (2002), pp.4571-4578.
DOI: 10.1364/ao.41.004571
Google Scholar
[6]
M. Fleischer, R. Windecker and H.J. Tiziani: Fast algorithms for data reduction in modern optical three-dimensional profile measurement system with MMX technology. App. Opt., 8 (2000), pp.1290-1297.
DOI: 10.1364/ao.39.001290
Google Scholar
[7]
G.S. Kino and S.S.C. Chim: Mirau correlation microscope. Appl. Opt., 29 (1990), pp.3775-3738.
DOI: 10.1364/ao.29.003775
Google Scholar
[8]
E.V. Sysoev: Partial Scanning of Correlogramms for Measurement of Surface Microreliefs. Optoelectronic, Instrumentation and Data Processing, Vol. 43, No. 1 (2007).
Google Scholar
[9]
M. Fleischer, R. Windecker, and H.J. Tiziani: Theoretical limits of scanning white-light interferometry signal evalution algorithms. Appl. Opt., 17 (2001), pp.2815-2820.
DOI: 10.1364/ao.40.002815
Google Scholar
[10]
Jan Niehues, Peter Lehmann: Dual-wavelength vertical scanning low-coherence interference microscopy. Proc. SPIE, Vol. 6616 (2007).
DOI: 10.1117/12.726108
Google Scholar