p.847
p.851
p.855
p.859
p.865
p.869
p.873
p.877
p.881
Subnanosecond Semiconductor Opening Switch Based on 4H-SiC Junction Diode
Abstract:
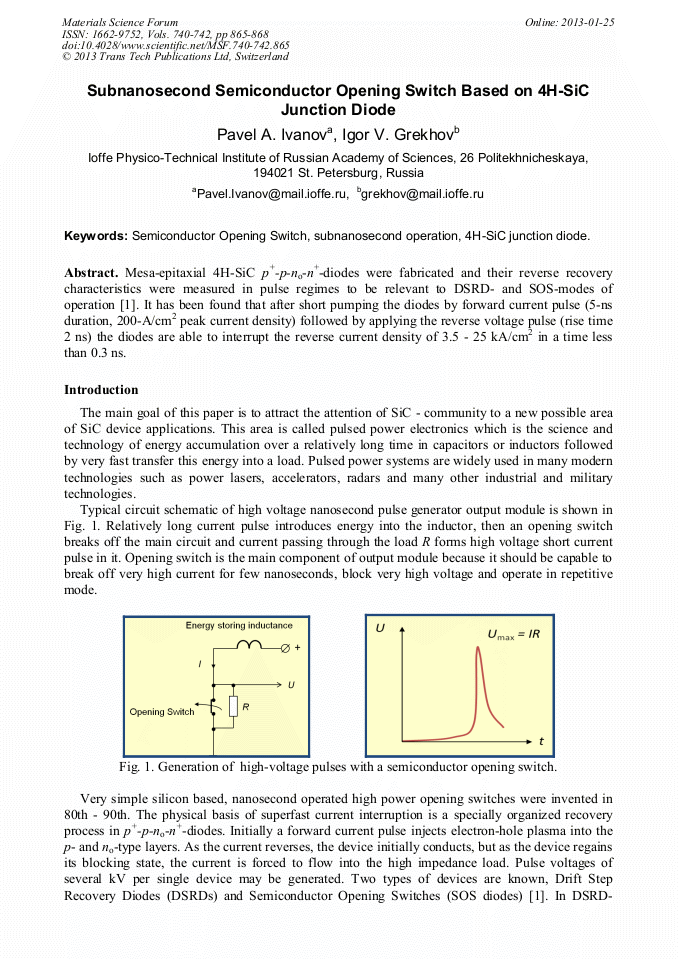
Mesa-epitaxial 4H-SiC p+-p-no-n+-diodes were fabricated and their reverse recovery characteristics were measured in pulse regimes to be relevant to DSRD- and SOS-modes of operation [I.V. Grekhov, G.A. Mesyats, Physical basis for high-power semiconductor nanosecond opening switches, IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science 28 (2000) 1540-1544]. It has been found that after short pumping the diodes by forward current pulse (5-ns duration, 200-A/cm2 peak current density) followed by applying the reverse voltage pulse (rise time 2 ns) the diodes are able to interrupt the reverse current density of 3.5 - 25 kA/cm2 in a time less than 0.3 ns.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
865-868
Citation:
Online since:
January 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: